Effects of decontamination, DNA extraction, and amplification procedures on the molecular diagnosis of Mycobacterium ulcerans disease (Buruli ulcer)
- PMID: 22259213
- PMCID: PMC3318535
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.05592-11
Effects of decontamination, DNA extraction, and amplification procedures on the molecular diagnosis of Mycobacterium ulcerans disease (Buruli ulcer)
Abstract
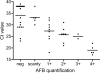
We compared two DNA extraction methods (a semiautomated method using a Maxwell kit and a modified Boom method) and three amplification procedures (a single-step PCR, a nested PCR, and a real-time quantitative PCR) on 74 surgical tissue specimens from patients with clinically suspected Buruli ulcer. All of these procedures were compared before and after decontamination. We observed that, among the procedures tested, real-time PCR after the modified Boom extraction method or a single-run PCR assay after the Maxwell 16 extraction method, performed on nondecontaminated suspensions, are the best for the molecular diagnosis of Mycobacterium ulcerans disease.
Figures

References
-
- Affolabi D. 2009. Development of simple and inexpensive tools for the control of mycobacterial diseases in a low-resource country. Ph.D. dissertation University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium
-
- American Thoracic Society 1981. Diagnostic standards and classification of tuberculosis and other mycobacterial diseases. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 123:343–358 - PubMed
-
- Beissner M, Herbinger KH, Bretzel G. 2010. Laboratory diagnosis of Buruli ulcer disease. Future Microbiol. 5:363–370 - PubMed
-
- Durnez L, et al. 2009. A comparison of DNA extraction procedures for the detection of Mycobacterium ulcerans, the causative agent of Buruli ulcer, in clinical and environmental specimens. J. Microbiol. Methods 76:152–158 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

