(Z)-3-(4-Chloro-phen-yl)-2-{[N-(2-formyl-phen-yl)-4-methyl-benzene-sulfonamido]-meth-yl}prop-2-ene-nitrile
- PMID: 22259557
- PMCID: PMC3254413
- DOI: 10.1107/S160053681105241X
(Z)-3-(4-Chloro-phen-yl)-2-{[N-(2-formyl-phen-yl)-4-methyl-benzene-sulfonamido]-meth-yl}prop-2-ene-nitrile
Abstract
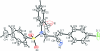
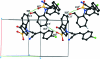
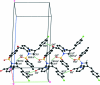
In the title compound, C(24)H(19)ClN(2)O(3)S, the sulfonyl-bound benzene ring forms dihedral angles of 38.1 (2) and 81.2 (1)°, respectively, with the formyl benzene and benzene rings. The mol-ecular conformation is stabilized by a weak intra-molecular C-H⋯O hydrogen bond, which generates an S(5) ring motif. The crystal packing is stabilized by C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, which generate C(7) zigzag chains along [010] and R(3) (3)(19) ring motifs along [010]. The crystal packing is further stabilized by C-Cl⋯π inter-actions [Cl⋯centroid = 3.456 (2) Å and C-Cl⋯centroid = 173.4 (2)°].
Figures

References
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT and XPREP Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
-
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
