Pure word deafness in a patient with early-onset Alzheimer's disease: an unusual presentation
- PMID: 22259620
- PMCID: PMC3259498
- DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2011.7.4.227
Pure word deafness in a patient with early-onset Alzheimer's disease: an unusual presentation
Abstract
Background and purpose: The occurrence of PWD in neurodegenerative disease is very rare, and this is the first report of it being related to early-onset AD. We describe a patient with early-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD) who presented with pure word deafness (PWD).
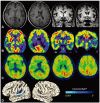
Case report: The patient had experienced PWD for 2 years, followed by other cognitive deficits suggestive of parietotemporal dysfunction. Brain imaging including (18)FDG-PET and [(11)C] PIB-PET supported the diagnosis of AD.
Conclusions: Our case highlights the clinical variability that characterizes early-onset AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; primary progressive aphasia; pure word deafness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Coslett HB, Brashear HR, Heilman KM. Pure word deafness after bilateral primary auditory cortex infarcts. Neurology. 1984;34:347–352. - PubMed
-
- Denes G, Semenza C. Auditory modality-specific anomia: evidence from a case of pure word deafness. Cortex. 1975;11:401–411. - PubMed
-
- Iizuka O, Suzuki K, Endo K, Fujii T, Mori E. Pure word deafness and pure anarthria in a patient with frontotemporal dementia. Eur J Neurol. 2007;14:473–475. - PubMed
-
- Otsuki M, Soma Y, Sato M, Homma A, Tsuji S. Slowly progressive pure word deafness. Eur Neurol. 1998;39:135–140. - PubMed
-
- Seo SW, Im K, Lee JM, Kim YH, Kim ST, Kim SY, et al. Cortical thickness in single- versus multiple-domain amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage. 2007;36:289–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

