Enhancement of Antinociception by Co-administrations of Nefopam, Morphine, and Nimesulide in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain
- PMID: 22259710
- PMCID: PMC3259142
- DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2012.25.1.7
Enhancement of Antinociception by Co-administrations of Nefopam, Morphine, and Nimesulide in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
Background: Neuropathic pain is a chronic pain due to disorder in the peripheral or central nervous system with different pathophysiological mechanisms. Current treatments are not effective. Analgesic drugs combined can reduce pain intensity and side effects. Here, we studied the analgesic effect of nimesulide, nefopam, and morphine with different mechanisms of action alone and in combination with other drugs in chronic constriction injury (CCI) model of neuropathic pain.
Methods: Male Wistar rats (n = 8) weighing 150-200 g were divided into 3 different groups: 1- Saline-treated CCI group, 2- Saline-treated sham group, and 3- Drug-treated CCI groups. Nimesulide (1.25, 2.5, and 5 mg/kg), nefopam (10, 20, and 30 mg/kg), and morphine (1, 3, and 5 mg/kg) were injected 30 minutes before surgery and continued daily to day 14 post-ligation. In the combination strategy, a nonanalgesic dose of drugs was used in combination such as nefopam + morphine, nefopam + nimesulide, and nimesulide + morphine. Von Frey filaments for mechanical allodynia and acetone test for cold allodynia were, respectively, used as pain behavioral tests. Experiments were performed on day 0 (before surgery) and days 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 post injury.
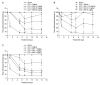
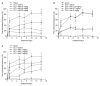
Results: Nefopam (30 mg/kg) and nimesulide (5 mg/kg) blocked mechanical and thermal allodynia; the analgesic effects of morphine (5 mg/kg) lasted for 7 days. Allodynia was completely inhibited in combination with nonanalgesic doses of nefopam (10 mg/kg), nimesulide (1.25 mg/kg), and morphine (3 mg/kg).
Conclusions: It seems that analgesic drugs used in combination, could effectively reduce pain behavior with reduced adverse effects.
Keywords: combination therapy; morphine; nefopam; neuropathy; nimesulide.
Figures
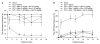
Similar articles
-
The attenuation of pain behaviour and serum interleukin-6 concentration by nimesulide in a rat model of neuropathic pain.Scand J Pain. 2010 Oct 1;1(4):229-234. doi: 10.1016/j.sjpain.2010.08.003. Scand J Pain. 2010. PMID: 29913996
-
Nefopam potentiates morphine antinociception in allodynia and hyperalgesia in the rat.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004 Apr;77(4):695-703. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2004.01.018. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004. PMID: 15099914
-
Post-injury repeated administrations of minocycline improve the antinociceptive effect of morphine in chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain in rat.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Oct;102(4):520-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.07.001. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012. PMID: 22789876
-
Nefopam analgesia and its role in multimodal analgesia: A review of preclinical and clinical studies.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Jan;43(1):3-12. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12506. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26475417 Review.
-
Rediscovery of nefopam for the treatment of neuropathic pain.Korean J Pain. 2014 Apr;27(2):103-11. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.2.103. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Korean J Pain. 2014. PMID: 24748937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The analgesic effect of nefopam with fentanyl at the end of laparoscopic cholecystectomy.Korean J Pain. 2013 Oct;26(4):361-7. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.361. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Korean J Pain. 2013. PMID: 24156002 Free PMC article.
-
A meta analysis of efficacy and safety of nefopam for laparoscopic cholecystectomy pain management.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2025 Mar 13;20(2):191-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2025.02.010. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40162100 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D3 receptor dysfunction prevents anti-nociceptive effects of morphine in the spinal cord.Front Neural Circuits. 2014 Jun 11;8:62. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00062. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2014. PMID: 24966815 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic inflammatory pain prevents tolerance to the antinociceptive effect of morphine microinjected into the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray of the rat.J Pain. 2013 Dec;14(12):1601-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Oct 22. J Pain. 2013. PMID: 24161274 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of nefopam on streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathic pain in rats.Korean J Pain. 2014 Oct;27(4):326-33. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.4.326. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Korean J Pain. 2014. PMID: 25317281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blackburn-Munro G. Pain-like behaviours in animals - how human are they? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25:299–305. - PubMed
-
- Schmader KE. Epidemiology and impact on quality of life of postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. Clin J Pain. 2002;18:350–354. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki R, Dickenson AH. Differential pharmacological modulation of the spontaneous stimulus-independent activity in the rat spinal cord following peripheral nerve injury. Exp Neurol. 2006;198:72–80. - PubMed
-
- Arnér S, Meyerson BA. Lack of analgesic effect of opioids on neuropathic and idiopathic forms of pain. Pain. 1988;33:11–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
