The Development of a Graphical User Interface Engine for the Convenient Use of the HL7 Version 2.x Interface Engine
- PMID: 22259723
- PMCID: PMC3259556
- DOI: 10.4258/hir.2011.17.4.214
The Development of a Graphical User Interface Engine for the Convenient Use of the HL7 Version 2.x Interface Engine
Abstract
Objectives: The Health Level Seven Interface Engine (HL7 IE), developed by Kyungpook National University, has been employed in health information systems, however users without a background in programming have reported difficulties in using it. Therefore, we developed a graphical user interface (GUI) engine to make the use of the HL7 IE more convenient.
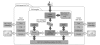
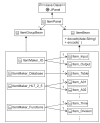
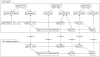
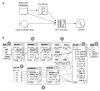
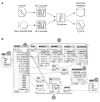
Methods: The GUI engine was directly connected with the HL7 IE to handle the HL7 version 2.x messages. Furthermore, the information exchange rules (called the mapping data), represented by a conceptual graph in the GUI engine, were transformed into program objects that were made available to the HL7 IE; the mapping data were stored as binary files for reuse. The usefulness of the GUI engine was examined through information exchange tests between an HL7 version 2.x message and a health information database system.
Results: Users could easily create HL7 version 2.x messages by creating a conceptual graph through the GUI engine without requiring assistance from programmers. In addition, time could be saved when creating new information exchange rules by reusing the stored mapping data.
Conclusions: The GUI engine was not able to incorporate information types (e.g., extensible markup language, XML) other than the HL7 version 2.x messages and the database, because it was designed exclusively for the HL7 IE protocol. However, in future work, by including additional parsers to manage XML-based information such as Continuity of Care Documents (CCD) and Continuity of Care Records (CCR), we plan to ensure that the GUI engine will be more widely accessible for the health field.
Keywords: Computer Graphics; Health Level Seven; Medical Informatics; Software Design.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



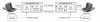

Similar articles
-
Development of an HL7 interface engine, based on tree structure and streaming algorithm, for large-size messages which include image data.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2005 Nov;80(2):126-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2005.07.004. Epub 2005 Sep 21. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2005. PMID: 16181703
-
A standards-based clinical information system for HIV/AIDS.Medinfo. 1995;8 Pt 1:402. Medinfo. 1995. PMID: 8591210
-
RGG: a general GUI Framework for R scripts.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Mar 2;10:74. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-74. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19254356 Free PMC article.
-
Using hub technology to facilitate information system integration in a health-care enterprise.Am J Clin Pathol. 1996 Apr;105(4 Suppl 1):S25-32. Am J Clin Pathol. 1996. PMID: 8607458 Review.
-
Some computer graphical user interfaces in radiation therapy.World J Radiol. 2016 Mar 28;8(3):255-67. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i3.255. World J Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27027225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a Multi-Agent m-Health Application Based on Various Protocols for Chronic Disease Self-Management.J Med Syst. 2016 Jan;40(1):36. doi: 10.1007/s10916-015-0401-5. Epub 2015 Nov 14. J Med Syst. 2016. PMID: 26573657
References
-
- Walker JM, Bieber EJ, Richards F. Implementing an electronic health record system. London, UK: Springer; 2005.
-
- Lopez DM, Blobel BG. A development framework for semantically interoperable health information systems. Int J Med Inform. 2009;78:83–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

