Diagnostic utility of osteocalcin, undercarboxylated osteocalcin, and alkaline phosphatase for osteoporosis in premenopausal and postmenopausal women
- PMID: 22259775
- PMCID: PMC3255495
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2012.32.1.23
Diagnostic utility of osteocalcin, undercarboxylated osteocalcin, and alkaline phosphatase for osteoporosis in premenopausal and postmenopausal women
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the diagnostic utility of osteocalcin (OC), undercarboxylated osteocalcin (ucOC), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in pre- and postmenopausal women for femoral neck, L1-4, and L2-4 bone mineral density (BMD) values by taking into consideration their age, body mass index (BMI), and menopausal status.
Methods: Premenopausal (N=40) and postmenopausal cases (N=42) were classified as 25-34 or 35-45 yr of age and within the first 5 yr or 5 yr or more after the onset of menopause, respectively.
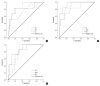
Results: Among the groups, statistical differences were found for age, BMI, OC, ucOC, ALP, femoral neck BMD, L1-4 BMD, and L2-4 BMD. The highest serum OC, ucOC, and ALP levels were observed in cases within the first 5 yr after the onset of menopause, probably due to a more rapid bone turnover rate. The best predictors for the femoral neck osteoporosis were ALP, OC, and calcium (areas under the ROC curve [AUC]=0.882, 0.829, and 0.761, respectively), and those for L1-4 and L2-4 osteoporosis were OC, ALP, and ucOC (AUC=0.949, 0.873, and 0.845; and 0.866, 0.819, and 0.814, respectively). Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that the most discriminative parameter for osteoporosis was OC.
Conclusions: These results indicate that serum OC levels, with or without ucOC and ALP, may be useful to monitor follow-up changes that currently cannot be assessed with BMD and to diagnose femoral neck, L1-4 spine, and L2-4 spine osteoporosis.
Keywords: Bone mineral density; Menopause; Osteocalcin; Osteoporosis; Undercarboxylated osteocalcin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
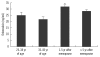
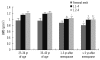
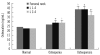
References
-
- NIH consensus development panel on osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy, March 7-29, 2000: highlights of the conference. South Med J. 2001;94:569–573. - PubMed
-
- Garnero P, Sornay-Rendu E, Chapuy MC, Delmas PD. Increased bone turnover in late postmenopausal women is a major determinant of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;3:337–349. - PubMed
-
- Christiansen C, Lindsay R. Estrogens, bone loss and preservation. Osteoporos Int. 1990;1:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Dalle Carbonare L, Giannini S. Bone microarchitecture as an important determinant of bone strength. J Endocrinol Invest. 2004;27:99–105. - PubMed
-
- Kanis JA. Diagnosis of osteoporosis and assessment of fracture risk. Lancet. 2002;359:1929–1936. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

