Neuroprotection with metformin and thymoquinone against ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in prenatal rat cortical neurons
- PMID: 22260211
- PMCID: PMC3317821
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-11
Neuroprotection with metformin and thymoquinone against ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in prenatal rat cortical neurons
Abstract
Background: Exposure to ethanol during early development triggers severe neuronal death by activating multiple stress pathways and causes neurological disorders, such as fetal alcohol effects or fetal alcohol syndrome. This study investigated the effect of ethanol on intracellular events that predispose developing neurons for apoptosis via calcium-mediated signaling. Although the underlying molecular mechanisms of ethanol neurotoxicity are not completely determined, mitochondrial dysfunction, altered calcium homeostasis and apoptosis-related proteins have been implicated in ethanol neurotoxicity. The present study was designed to evaluate the neuroprotective mechanisms of metformin (Met) and thymoquinone (TQ) during ethanol toxicity in rat prenatal cortical neurons at gestational day (GD) 17.5.
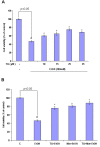
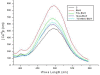
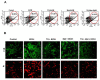
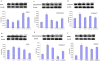
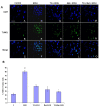
Results: We found that Met and TQ, separately and synergistically, increased cell viability after ethanol (100 mM) exposure for 12 hours and attenuated the elevation of cytosolic free calcium [Ca²⁺]c. Furthermore, Met and TQ maintained normal physiological mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ΔψM), which is typically lowered by ethanol exposure. Increased cytosolic free [Ca²⁺]c and lowered mitochondrial transmembrane potential after ethanol exposure significantly decreased the expression of a key anti-apoptotic protein (Bcl-2), increased expression of Bax, and stimulated the release of cytochrome-c from mitochondria. Met and TQ treatment inhibited the apoptotic cascade by increasing Bcl-2 expression. These compounds also repressed the activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 and reduced the cleavage of PARP-1. Morphological conformation of cell death was assessed by TUNEL, Fluoro-Jade-B, and PI staining. These staining methods demonstrated more cell death after ethanol treatment, while Met, TQ or Met plus TQ prevented ethanol-induced apoptotic cell death.
Conclusion: These findings suggested that Met and TQ are strong protective agents against ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis in primary rat cortical neurons. The collective data demonstrated that Met and TQ have the potential to ameliorate ethanol neurotoxicity and revealed a possible protective target mechanism for the damaging effects of ethanol during early brain development.
Figures
References
-
- Jones KL, Smith DW, Ulleland CN, Streissguth AP. Pattern of malformation in offspring of chronic alcoholic mothers. Lancet. 1973;1:1267–1271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

