TGF-β1 modulates the homeostasis between MMPs and MMP inhibitors through p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 in highly invasive breast cancer cells
- PMID: 22260435
- PMCID: PMC3277461
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-26
TGF-β1 modulates the homeostasis between MMPs and MMP inhibitors through p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 in highly invasive breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Metastasis is the main factor responsible for death in breast cancer patients. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors, known as tissue inhibitors of MMPs (TIMPs), and the membrane-associated MMP inhibitor (RECK), are essential for the metastatic process. We have previously shown a positive correlation between MMPs and their inhibitors expression during breast cancer progression; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying this coordinate regulation remain unknown. In this report, we investigated whether TGF-β1 could be a common regulator for MMPs, TIMPs and RECK in human breast cancer cell models.
Methods: The mRNA expression levels of TGF-β isoforms and their receptors were analyzed by qRT-PCR in a panel of five human breast cancer cell lines displaying different degrees of invasiveness and metastatic potential. The highly invasive MDA-MB-231 cell line was treated with different concentrations of recombinant TGF-β1 and also with pharmacological inhibitors of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2. The migratory and invasive potential of these treated cells were examined in vitro by transwell assays.
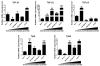
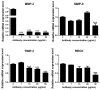
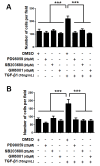
Results: In general, TGF-β2, TβRI and TβRII are over-expressed in more aggressive cells, except for TβRI, which was also highly expressed in ZR-75-1 cells. In addition, TGF-β1-treated MDA-MB-231 cells presented significantly increased mRNA expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, MMP-14, TIMP-2 and RECK. TGF-β1 also increased TIMP-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9 protein levels but downregulated RECK expression. Furthermore, we analyzed the involvement of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2, representing two well established Smad-independent pathways, in the proposed mechanism. Inhibition of p38MAPK blocked TGF-β1-increased mRNA expression of all MMPs and MMP inhibitors analyzed, and prevented TGF-β1 upregulation of TIMP-2 and MMP-2 proteins. Moreover, ERK1/2 inhibition increased RECK and prevented the TGF-β1 induction of pro-MMP-9 and TIMP-2 proteins. TGF-β1-enhanced migration and invasion capacities were blocked by p38MAPK, ERK1/2 and MMP inhibitors.
Conclusion: Altogether, our results support that TGF-β1 modulates the mRNA and protein levels of MMPs (MMP-2 and MMP-9) as much as their inhibitors (TIMP-2 and RECK). Therefore, this cytokine plays a crucial role in breast cancer progression by modulating key elements of ECM homeostasis control. Thus, although the complexity of this signaling network, TGF-β1 still remains a promising target for breast cancer treatment.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Correlation between MMPs and their inhibitors in breast cancer tumor tissue specimens and in cell lines with different metastatic potential.BMC Cancer. 2009 Jan 14;9:20. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-20. BMC Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19144199 Free PMC article.
-
ERK1/2 and p38 MAP kinase control MMP-2, MT1-MMP, and TIMP action and affect cell migration: a comparison between mesothelioma and mesothelial cells.J Cell Physiol. 2006 May;207(2):540-52. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20605. J Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16447244
-
Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 expression via activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Sp1 in human fibrosarcoma cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2006 Mar;4(3):209-20. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-05-0140. Mol Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16547158
-
Expression and regulation of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration.Spine J. 2013 Mar;13(3):331-41. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2012.02.027. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Spine J. 2013. PMID: 23369495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The behavior of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in colorectal cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Oct 16;13(10):13240-63. doi: 10.3390/ijms131013240. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23202950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CIP4 promotes metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer and is associated with poor patient prognosis.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 20;6(11):9397-408. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3351. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25823823 Free PMC article.
-
Methanolic Phoenix dactylifera L. Extract Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Hepatic Injury in Male Rats.Nutrients. 2022 Feb 28;14(5):1025. doi: 10.3390/nu14051025. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35268000 Free PMC article.
-
The Extracellular Matrix: Its Composition, Function, Remodeling, and Role in Tumorigenesis.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Apr 5;8(2):146. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8020146. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37092398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P38 kinase in gastrointestinal cancers.Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 Sep;30(9):1181-1189. doi: 10.1038/s41417-023-00622-1. Epub 2023 May 29. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023. PMID: 37248432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Keratoconus Cell Contractility is Mediated by Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Isoforms.J Funct Biomater. 2015 Jun 18;6(2):422-38. doi: 10.3390/jfb6020422. J Funct Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26096146 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

