Transcriptional ontogeny of the developing liver
- PMID: 22260730
- PMCID: PMC3306746
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-33
Transcriptional ontogeny of the developing liver
Abstract
Background: During embryogenesis the liver is derived from endodermal cells lining the digestive tract. These endodermal progenitor cells contribute to forming the parenchyma of a number of organs including the liver and pancreas. Early in organogenesis the fetal liver is populated by hematopoietic stem cells, the source for a number of blood cells including nucleated erythrocytes. A comprehensive analysis of the transcriptional changes that occur during the early stages of development to adulthood in the liver was carried out.
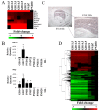
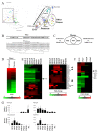
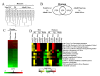
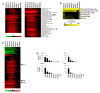
Results: We characterized gene expression changes in the developing mouse liver at gestational days (GD) 11.5, 12.5, 13.5, 14.5, 16.5, and 19 and in the neonate (postnatal day (PND) 7 and 32) compared to that in the adult liver (PND67) using full-genome microarrays. The fetal liver, and to a lesser extent the neonatal liver, exhibited dramatic differences in gene expression compared to adults. Canonical pathway analysis of the fetal liver signature demonstrated increases in functions important in cell replication and DNA fidelity whereas most metabolic pathways of intermediary metabolism were under expressed. Comparison of the dataset to a number of previously published microarray datasets revealed 1) a striking similarity between the fetal liver and that of the pancreas in both mice and humans, 2) a nucleated erythrocyte signature in the fetus and 3) under expression of most xenobiotic metabolism genes throughout development, with the exception of a number of transporters associated with either hematopoietic cells or cell proliferation in hepatocytes.
Conclusions: Overall, these findings reveal the complexity of gene expression changes during liver development and maturation, and provide a foundation to predict responses to chemical and drug exposure as a function of early life-stages.
Figures

References
-
- Zorn A. In: Stem Book. Melton DaG, L, editor. 2009. Liver Development.
-
- Slack JM. Developmental biology of the pancreas. Development. 1995;121(6):1569–1580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

