Flow cytometric immunophenotypic assessment of T-cell clonality by vβ repertoire analysis in fine-needle aspirates and cerebrospinal fluid
- PMID: 22261447
- PMCID: PMC7479924
- DOI: 10.1309/AJCPPT93VZMAREHK
Flow cytometric immunophenotypic assessment of T-cell clonality by vβ repertoire analysis in fine-needle aspirates and cerebrospinal fluid
Abstract
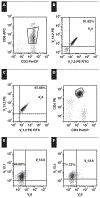
Flow cytometric T-cell receptor V(β) repertoire analysis (TCR-V(β)-R) is a sensitive method to detect T-cell clonality; however, its implementation in low-cellularity specimens has not been established. We developed a strategy to use TCR-V(β)-R in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and fine-needle aspirate (FNA) specimens. Initially, full TCR-V(β)-R was evaluated in diagnostic/screening specimens from 8 patients with T-cell neoplasia to determine tumor-specific TCR-V(β) protein expression. Subsequently, an abbreviated, patient-specific TCR-V(β)-R evaluation was performed in 17 paucicellular specimens from the patients (8 CSF, 9 FNA) for staging and monitoring of minimal residual disease (MRD). A single cocktail containing 3 anti-V(β) antibodies (1 tumor-specific and 2 negative controls) in combination with other antibodies chosen to help gate on atypical T cells is highly sensitive and specific for detecting low-level neoplastic T-cell involvement in paucicellular specimens. This TCR-V(β)-R strategy is valuable in staging and evaluating MRD in patients with T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Figures
References
-
- Meda BA, Buss DH, Woodruff RD, et al. Diagnosis and subclassification of primary and recurrent lymphoma: the usefulness and limitations of combined fine-needle aspiration cytomorphology and flow cytometry. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000;113:688–699. - PubMed
-
- Dong HY, Harris NL, Preffer FI, et al. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis and classification of primary and recurrent lymphoma: a retrospective analysis of the utility of cytomorphology and flow cytometry. Mod Pathol. 2001;14:472–481. - PubMed
-
- Dahmoush L, Hijazi Y, Barnes E, et al. Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: a cytopathologic, immunocytochemical, and flow cytometric study. Cancer. 2002;96:110–116. - PubMed
-
- Hegde U, Filie A, Little RF, et al. High incidence of occult leptomeningeal disease detected by flow cytometry in newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas at risk for central nervous system involvement: the role of flow cytometry versus cytology. Blood. 2005;105:496–502. - PubMed
-
- Quijano S, Lopez A, Manuel Sancho J, et al. Identification of leptomeningeal disease in aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: improved sensitivity of flow cytometry. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1462–1469. - PubMed

