Chronic direct renin inhibition with aliskiren prevents the development of hypertension in Cyp1a1-Ren2 transgenic rats with inducible ANG II-dependent hypertension
- PMID: 22261625
- PMCID: PMC3335984
- DOI: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3182410d1e
Chronic direct renin inhibition with aliskiren prevents the development of hypertension in Cyp1a1-Ren2 transgenic rats with inducible ANG II-dependent hypertension
Abstract
Introduction: This study was performed to determine whether chronic direct renin inhibition can prevent the development of slowly progressive angiotensin (ANG) II-dependent hypertension and the associated derangements in renal function in Cyplal-Ren2 transgenic rats with inducible expression of the Ren2 gene.
Methods: Male Cyplal-Ren2 rats (n = 6) were fed a normal diet containing 0.15% indole-3-carbinol (I3C) for 16 days to induce slowly progressive ANG II-dependent hypertension. Conscious systolic blood pressure was measured daily using tail-cuff plethysmography. The rats were then anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium and surgically prepared for the measurement of mean arterial pressure (MAP) and renal hemodynamics and excretory function.
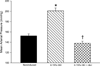
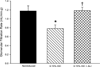
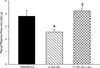
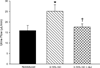
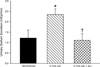
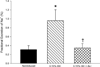
Results: In rats induced with I3C, systolic blood pressure increased by day 3 (130 ± 7-160 ± 5 mm Hg, P < 0.01) and continued to increase to 191 ± 6 mm Hg (P < 0.001) by day 16. In a separate group of rats (n = 6), chronic administration of the direct renin inhibitor, aliskiren (30 mg/kg/d, sc), prevented the development of hypertension (113 ± 5 versus 114 ± 5 mm Hg, not significant). Rats treated with aliskiren exhibited significantly lower mean arterial pressure (138 ± 4 versus 201 ± 6 mm Hg, P < 0.001), renal vascular resistance (23 ± 4 versus 38 ± 3 mm Hg/mL/min · g, P < 0.01), urine flow (17.6 ± 1.4 versus 25.1 ± 2.9 μL/min, P < 0.05) and urinary sodium excretion (1.11 ± 0.32 versus 2.35 ± 0.28 μEq/min, P < 0.05) and higher renal plasma flow (4.22 ± 0.23 versus 2.56 ± 0.21 mL/min · g, P < 0.01) and glomerular filtration rate (1.19 ± 0.07 versus 0.78 ± 0.08 mL/min · g, P< 0.01), compared with induced rats not treated chronically with aliskiren.
Conclusions: The present findings demonstrate that chronic direct renin inhibition with aliskiren prevents the development of ANG II-dependent hypertension and the associated derangements in renal hemodynamics and excretory function in Cyplal-Ren2 transgenic rats.
Figures



References
-
- Kantachuvesiri S, Fleming S, Peters J, et al. Controlled hypertension, a transgenic toggle switch reveals differential mechanisms underlying vascular disease. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36727–36733. - PubMed
-
- Campbell SJ, Carlotti F, Hall PA, et al. Regulation of the CYP1A1 promoter in transgenic mice: an exquisitely sensitive on-off system for cell specific gene regulation. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:2619–2625. - PubMed
-
- Gelboin HV. Benzo[alpha]pyrene metabolism, activation and carcinogenesis: role and regulation of mixed-function oxidases and related enzymes. Physiol Rev. 1980;60:1107–1166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

