Metaboloepigenetics: interrelationships between energy metabolism and epigenetic control of gene expression
- PMID: 22261928
- PMCID: PMC3338882
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.24054
Metaboloepigenetics: interrelationships between energy metabolism and epigenetic control of gene expression
Abstract
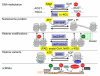
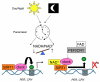
Diet and energy metabolism affect gene expression, which influences human health and disease. Here, we discuss the role of epigenetics as a mechanistic link between energy metabolism and control of gene expression. A number of key energy metabolites including SAM, acetyl-CoA, NAD(+), and ATP serve as essential co-factors for many, perhaps most, epigenetic enzymes that regulate DNA methylation, posttranslational histone modifications, and nucleosome position. The relative abundance of these energy metabolites allows a cell to sense its energetic state. And as co-factors, energy metabolites act as rheostats to modulate the activity of epigenetic enzymes and upregulate/downregulate transcription as appropriate to maintain homeostasis.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Prevention of neural tube defects: results of the Medical Research Council Vitamin Study. MRC Vitamin Study Research Group. Lancet. 1991;338(8760):131–137. - PubMed
-
- Burnett C, Valentini S, Cabreiro F, Goss M, Somogyvari M, Piper MD, Hoddinott M, Sutphin GL, Leko V, McElwee JJ, Vazquez-Manrique RP, Orfila AM, Ackerman D, Au C, Vinti G, Riesen M, Howard K, Neri C, Bedalov A, Kaeberlein M, Soti C, Partridge L, Gems D. Absence of effects of Sir2 overexpression on lifespan in C. elegans and Drosophila. Nature. 477(7365):482–485. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

