RNA therapeutics: beyond RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides
- PMID: 22262036
- PMCID: PMC4743652
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd3625
RNA therapeutics: beyond RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides
Abstract
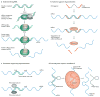
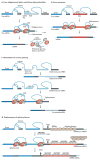
Here, we discuss three RNA-based therapeutic technologies exploiting various oligonucleotides that bind to RNA by base pairing in a sequence-specific manner yet have different mechanisms of action and effects. RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides downregulate gene expression by inducing enzyme-dependent degradation of targeted mRNA. Steric-blocking oligonucleotides block the access of cellular machinery to pre-mRNA and mRNA without degrading the RNA. Through this mechanism, steric-blocking oligonucleotides can redirect alternative splicing, repair defective RNA, restore protein production or downregulate gene expression. Moreover, they can be extensively chemically modified to acquire more drug-like properties. The ability of RNA-blocking oligonucleotides to restore gene function makes them best suited for the treatment of genetic disorders. Positive results from clinical trials for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy show that this technology is close to achieving its clinical potential.
Figures

References
-
- Goodchild J. Therapeutic oligonucleotides. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;764:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Crooke ST. Vitravene — another piece in the mosaic. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1998;8:vii–viii. - PubMed
-
- Moshfeghi AA, Puliafito CA. Pegaptanib sodium for the treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;14:671–682. - PubMed
-
- Fire A, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

