Physiology of incretins in health and disease
- PMID: 22262068
- PMCID: PMC3280665
- DOI: 10.1900/RDS.2011.8.293
Physiology of incretins in health and disease
Abstract
The incretin hormones, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), are gut peptides which are secreted by endocrine cells in the intestinal mucosa. Their plasma concentrations increase quickly following food ingestion, and carbohydrate, fat, and protein have all been shown to stimulate GLP-1 and GIP secretion. Although neural and hormonal mechanisms have also been proposed to regulate incretin hormone secretion, direct stimulation of the enteroendocrine cells by the presence of nutrients in the intestinal lumen is probably the most important factor in humans. The actions of the incretin hormones are crucial for maintaining normal islet function and glucose homeostasis. Furthermore, it is also now being recognized that incretin hormones may have other actions in addition to their glucoregulatory effects. Studies have shown that GLP-1 and GIP levels and actions may be perturbed in disease states, but interpretation of the precise relationship between disease and incretins is difficult. The balance of evidence seems to suggest that alterations in secretion and/or action of incretin hormones arise secondarily to the development of insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and/or increases in body weight rather than being causative factors. However, these impairments may contribute to the deterioration of glycemic control in diabetic patients.
Copyright © by Lab & Life Press/SBDR
Figures

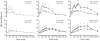
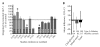
References
-
- Creutzfeldt W. The incretin concept today. Diabetologia. 1979;16:75–85. - PubMed
-
- Nauck MA, Homberger E, Siegel EG, Allen RC, Eaton RP, Ebert R, Creutzfeldt W. Incretin effects of increasing glucose loads in man calculated from venous insulin and C-peptide responses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986;63:492–498. - PubMed
-
- Lindgren O, Carr RD, Deacon CF, Holst JJ, Pacini G, Mari A, Ahren B. Incretin hormone and insulin responses to oral versus intravenous lipid administration in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:2519–2524. - PubMed
-
- Eissele R, Göke R, Willemer S, Harthus HP, Vermeer H, Arnold R, Göke B. Glucagon-like peptide-1 cells in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas of rat, pig and man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992;22:283–291. - PubMed
-
- Mortensen K, Christensen LL, Holst JJ, Orskov C. GLP-1 and GIP are colocalized in a subset of endocrine cells in the small intestine. Regul Pept. 2003;114:189–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
