Pulmonary artery embolization of intravenous leiomyomatosis extending into the right atrium
- PMID: 22263160
- PMCID: PMC3249311
- DOI: 10.5090/kjtcs.2011.44.3.243
Pulmonary artery embolization of intravenous leiomyomatosis extending into the right atrium
Abstract
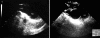
A 43-year-old woman was diagnosed with an intravenous leiomyomatosis at a previous hospital and transferred to our hospital to undergo surgical treatment. Emergency one-stage operation for coincidental removal of intra-abdominal, right atrial, and intravenous masses were planned. Upon arriving at the operating room, she suffered a sudden onset of severe dyspnea and showed hemodynamic instability. Intraoperative TEE showed pulmonary embolization of a right atrial mass. Removal of the pulmonary artery mass and the intra-abdominal mass, and the cardiopulmonary bypass were performed without any complications.
Keywords: Embolization; Leiomyomatosis; Pulmonary artery.
Figures


References
-
- Rispoli P, Santovito D, Tallia C, Varetto G, Conforti M, Rinaldi M. A one-stage approach to the treatment of intravenous leiomyomatosis extending to the right heart. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52:212–215. - PubMed
-
- Nam MS, Jeon MJ, Kim YT, Kim JW, Park KH, Hong YS. Pelvic leiomyomatosis with intracaval and intracardiac extension: a case report and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol. 2003;89:175–180. - PubMed
-
- Uchida H, Hattori Y, Nakada K, Iida T. Successful one-stage radical removal of intravenous leiomyomatosis extending to the right ventricle. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;103:1068–1070. - PubMed
-
- Harris LM, Karakousis CP. Intravenous leiomyomatosis with cardiac extension: tumor thrombectomy through an abdominal approach. J Vasc Surg. 2000;31:1046–1051. - PubMed
-
- Lo KW, Lau TK. Intracardiac leiomyomatosis. Case report and literature review. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2001;264:209–210. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources