Additive effects of sonic hedgehog and Nell-1 signaling in osteogenic versus adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells
- PMID: 22264144
- PMCID: PMC3411358
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2011.0461
Additive effects of sonic hedgehog and Nell-1 signaling in osteogenic versus adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells
Abstract
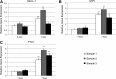
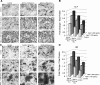
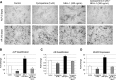
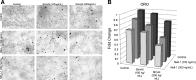
A theoretical inverse relationship exists between osteogenic (bone forming) and adipogenic (fat forming) mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) differentiation. This inverse relationship in theory partially underlies the clinical entity of osteoporosis, in which marrow MSCs have a preference for adipose differentiation that increases with age. Two pro-osteogenic cytokines have been recently studied that each also possesses antiadipogenic properties: Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) and NELL-1 proteins. In the present study, we assayed the potential additive effects of the biologically active N-terminus of SHH (SHH-N) and NELL-1 protein on osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of human primary adipose-derived stromal cell (hASCs). We observed that both recombinant SHH-N and NELL-1 protein significantly enhanced osteogenic differentiation and reduced adipose differentiation across all markers examined (alkaline phosphatase, Alizarin red and Oil red O staining, and osteogenic gene expression). Moreover, SHH-N and NELL-1 directed signaling produced additive effects on the pro-osteogenic and antiadipogenic differentiation of hASCs. NELL-1 treatment increased Hedgehog signaling pathway expression; coapplication of the Smoothened antagonist Cyclopamine reversed the pro-osteogenic effect of NELL-1. In summary, Hedgehog and Nell-1 signaling exert additive effects on the pro-osteogenic and antiadipogenic differentiation of ASCs. These studies suggest that the combination cytokines SHH-N+NELL-1 may represent a viable future technique for inducing the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs.
Figures


References
-
- Gimble JM. Zvonic S. Floyd ZE. Kassem M. Nuttall ME. Playing with bone and fat. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98:251–266. - PubMed
-
- Kirkland JL. Tchkonia T. Pirtskhalava T. Han J. Karagiannides I. Adipogenesis and aging: does aging make fat go MAD? Exp Gerontol. 2002;37:757–767. - PubMed
-
- Gimble JM. Nuttall ME. Bone and fat: old questions, new insights. Endocrine. 2004;23:183–188. - PubMed
-
- Neumann K. Endres M. Ringe J. Flath B. Manz R. Haupl T. Sittinger M. Kaps C. BMP7 promotes adipogenic but not osteo-/chondrogenic differentiation of adult human bone marrow-derived stem cells in high-density micro-mass culture. J Cell Biochem. 2007;102:626–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

