Activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin induces functional kinin B(1) receptor in rat spinal cord microglia
- PMID: 22264228
- PMCID: PMC3282640
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-16
Activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin induces functional kinin B(1) receptor in rat spinal cord microglia
Abstract
Background: The kinin B(1) receptor (B(1)R) is upregulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxydative stress, which are enhanced by transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 (TRPV1) activation. To examine the link between TRPV1 and B(1)R in inflammatory pain, this study aimed to determine the ability of TRPV1 to regulate microglial B(1)R expression in the spinal cord dorsal horn, and the underlying mechanism.
Methods: B(1)R expression (mRNA, protein and binding sites) was measured in cervical, thoracic and lumbar spinal cord in response to TRPV1 activation by systemic capsaicin (1-50 mg/kg, s.c) in rats pre-treated with TRPV1 antagonists (capsazepine or SB-366791), the antioxidant N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), or vehicle. B(1)R function was assessed using a tail-flick test after intrathecal (i.t.) injection of a selective B(1)R agonist (des-Arg(9)-BK), and its microglial localization was investigated by confocal microscopy with the selective fluorescent B(1)R agonist, [Nα-bodipy]-des-Arg(9)-BK. The effect of i.t. capsaicin (1 μg/site) was also investigated.
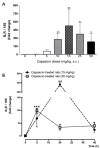
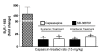
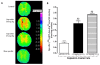
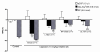
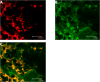
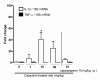
Results: Capsaicin (10 to 50 mg/kg, s.c.) enhanced time-dependently (0-24h) B(1)R mRNA levels in the lumbar spinal cord; this effect was prevented by capsazepine (10 mg/kg, i.p.; 10 μg/site, i.t.) and SB-366791 (1 mg/kg, i.p.; 30 μg/site, i.t.). Increases of B(1)R mRNA were correlated with IL-1β mRNA levels, and they were significantly less in cervical and thoracic spinal cord. Intrathecal capsaicin (1 μg/site) also enhanced B(1)R mRNA in lumbar spinal cord. NAC (1 g/kg/d × 7 days) prevented B(1)R up-regulation, superoxide anion production and NF-kB activation induced by capsaicin (15 mg/kg). Des-Arg(9)-BK (9.6 nmol/site, i.t.) decreased by 25-30% the nociceptive threshold at 1 min post-injection in capsaicin-treated rats (10-50 mg/kg) while it was without effect in control rats. Des-Arg(9)-BK-induced thermal hyperalgesia was blocked by capsazepine, SB-366791 and by antagonists/inhibitors of B(1)R (SSR240612, 10 mg/kg, p.o.), glutamate NMDA receptor (DL-AP5, 10 μg/site, i.t.), substance P NK-1 receptor (RP-67580, 10 μg/site, i.t.) and nitric oxide synthase (L-NNA, 10 μg/site, i.t.). The B(1)R fluorescent agonist was co-localized with an immunomarker of microglia (Iba-1) in spinal cord dorsal horn of capsaicin-treated rats.
Conclusion: This study highlights a new mechanism for B(1)R induction via TRPV1 activation and establishes a link between these two pro-nociceptive receptors in inflammatory pain.
Figures



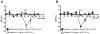
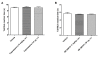


Similar articles
-
Reciprocal Regulatory Interaction between TRPV1 and Kinin B1 Receptor in a Rat Neuropathic Pain Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 27;21(3):821. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030821. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32012798 Free PMC article.
-
Key role for spinal dorsal horn microglial kinin B1 receptor in early diabetic pain neuropathy.J Neuroinflammation. 2010 Jun 29;7(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-36. J Neuroinflammation. 2010. PMID: 20587056 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular localization of kinin B1 receptor in the spinal cord of streptozotocin-diabetic rats with a fluorescent [Nalpha-Bodipy]-des-Arg9-bradykinin.J Neuroinflammation. 2009 Mar 26;6:11. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-6-11. J Neuroinflammation. 2009. PMID: 19323833 Free PMC article.
-
Capsaicin, The Vanilloid Receptor TRPV1 Agonist in Neuroprotection: Mechanisms Involved and Significance.Neurochem Res. 2023 Nov;48(11):3296-3315. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03983-z. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 37493882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capsaicin and TRPV1 Channels in the Cardiovascular System: The Role of Inflammation.Cells. 2021 Dec 22;11(1):18. doi: 10.3390/cells11010018. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011580 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease: A Role for Ion Channels.Front Neurosci. 2018 Sep 28;12:676. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00676. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30323735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory effect of intrathecally administered AM404, an endocannabinoid reuptake inhibitor, on neuropathic pain in a rat chronic constriction injury model.Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Jun;73(3):820-827. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00250-2. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Pharmacol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33783763
-
TRPV1: a stress response protein in the central nervous system.Am J Neurodegener Dis. 2012;1(1):1-14. Epub 2012 Apr 1. Am J Neurodegener Dis. 2012. PMID: 22737633 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal Regulatory Interaction between TRPV1 and Kinin B1 Receptor in a Rat Neuropathic Pain Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 27;21(3):821. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030821. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32012798 Free PMC article.
-
Tibial post fracture pain is reduced in kinin receptors deficient mice and blunted by kinin receptor antagonists.J Transl Med. 2019 Oct 22;17(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-2095-9. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31640792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Regoli D, Barabe J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980;32:1–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

