Development of a TaqMan Allelic Discrimination assay for detection of single nucleotides polymorphisms associated with anti-malarial drug resistance
- PMID: 22264294
- PMCID: PMC3273427
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-23
Development of a TaqMan Allelic Discrimination assay for detection of single nucleotides polymorphisms associated with anti-malarial drug resistance
Abstract
Background: Anti-malarial drug resistance poses a threat to current global efforts towards control and elimination of malaria. Several methods are used in monitoring anti-malarial drug resistance. Molecular markers such as single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) for example are increasingly being used to identify genetic mutations related to anti-malarial drug resistance. Several methods are currently being used in analysis of SNP associated with anti-malarial drug resistance and although each one of these methods has unique strengths and shortcoming, there is still need to improve and/or develop new methods that will close the gap found in the current methods.
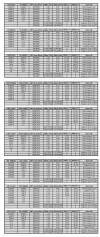
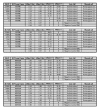
Methods: TaqMan Allelic Discrimination assays for detection of SNPs associated with anti-malarial drug resistance were designed for analysis on Applied Biosystems PCR platform. These assays were designed by submitting SNP sequences associated with anti-malarial drug resistance to Applied Biosystems website. Eleven SNPs associated with resistance to anti-malarial drugs were selected and tested. The performance of each SNP assay was tested by creating plasmid DNAs carrying codons of interests and analysing them for analysis. To test the sensitivity and specificity of each SNP assay, 12 clinical samples were sequenced at codons of interest and used in the analysis. Plasmid DNAs were used to establish the Limit of Detection (LoD) for each assay.
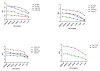
Results: Data from genetic profiles of the Plasmodium falciparum laboratory strains and sequence data from 12 clinical samples was used as the reference method with which the performance of the SNP assays were compared to. The sensitivity and specificity of each SNP assay was establish at 100%. LoD for each assay was established at 2 GE, equivalent to less than 1 parasite/μL. SNP assays performed well in detecting mixed infection and analysis of clinical samples.
Conclusion: TaqMan Allelic Discrimination assay provides a good alternative tool in detection of SNPs associated with anti-malarial drug.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-throughput genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the Plasmodium falciparum dhfr gene by asymmetric PCR and melt-curve analysis.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Sep;48(9):3081-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00634-10. Epub 2010 Jul 14. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20631115 Free PMC article.
-
A multiplex ligase detection reaction-fluorescent microsphere assay for simultaneous detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with Plasmodium falciparum drug resistance.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Mar;45(3):752-61. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01683-06. Epub 2006 Nov 22. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17121999 Free PMC article.
-
Tools for surveillance of anti-malarial drug resistance: an assessment of the current landscape.Malar J. 2018 Feb 8;17(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2185-9. Malar J. 2018. PMID: 29422048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance of molecular inversion probe DR23K and Paragon MAD4HatTeR Amplicon sequencing panels for detection of Plasmodium falciparum mutations associated with antimalarial drug resistance.Malar J. 2025 Jun 12;24(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12936-025-05441-3. Malar J. 2025. PMID: 40506703 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of copy number variation in genes related to anti-malarial drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum.Gene. 2020 Apr 30;736:144414. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144414. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32006594 Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of the ligase detection reaction fluorescent microsphere assay for the detection of Plasmodium falciparum resistance mediating polymorphisms in Uganda.Malar J. 2014 Mar 14;13:95. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-95. Malar J. 2014. PMID: 24629020 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a TaqMan® Allelic Discrimination qPCR Assay for Rapid Detection of Equine CXCL16 Allelic Variants Associated With the Establishment of Long-Term Equine Arteritis Virus Carrier State in Stallions.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 13;13:871875. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.871875. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35495124 Free PMC article.
-
High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology.Sci Rep. 2017 May 25;7(1):2398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02724-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28546554 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a ligase detection reaction-fluorescent microsphere assay for characterization of resistance-mediating polymorphisms in African samples of Plasmodium falciparum.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Aug;51(8):2564-70. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00904-13. Epub 2013 May 29. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23720790 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex qPCR for detection and absolute quantification of malaria.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 29;8(8):e71539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071539. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24009663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olliaro P. Drug resistance hampers our capacity to roll back malaria. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;15:247–257. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global report on antimalarial drug efficacy and drug resistance. World Health Organization, Geneva; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

