A polymorphism associated with depressive disorders differentially regulates brain derived neurotrophic factor promoter IV activity
- PMID: 22265241
- PMCID: PMC3712170
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.11.030
A polymorphism associated with depressive disorders differentially regulates brain derived neurotrophic factor promoter IV activity
Abstract
Background: Changes in brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression have been associated with mood disorders and cognitive dysfunction. Transgenic models that overexpress or underexpress BDNF demonstrate similar deficits in cognition and mood. We explored the hypothesis that BDNF expression is controlled by balancing the activity of BDNF promoter IV (BP4) with a negative regulatory region containing a polymorphism associated with cognitive dysfunction and mood disorders.
Methods: We used comparative genomics, transgenic mouse production, and magnetofection of primary neurons with luciferase reporters and signal transduction agonist treatments to identify novel polymorphic cis-regulatory regions that control BP4 activity.
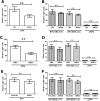
Results: We show that BP4 is active in the hippocampus, the cortex, and the amygdala and responds strongly to stimuli such as potassium chloride, lithium chloride, and protein kinase C agonists. We also identified a highly conserved sequence 21 kilobase 5' of BP4 that we called BE5.2, which contains rs12273363, a polymorphism associated with decreased BDNF expression, mood disorders, and cognitive decline. BE5.2 modulated the ability of BP4 to respond to different stimuli. Intriguingly, the rarer disease associated allele, BE5.2(C), acted as a significantly stronger repressor of BP4 activity than the more common BE5.2(T) allele.
Conclusions: This study shows that the C allele of rs12273363, which is associated with mood disorder, modulates BP4 activity in an allele-specific manner following cell depolarization or the combined activity of protein kinase A and protein kinase C pathways. The relevance of these findings to the role of BDNF misexpression in mood disorders and cognitive decline is discussed.
Copyright © 2012 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





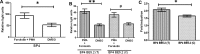
Similar articles
-
An ancient polymorphic regulatory region within the BDNF gene associated with obesity modulates anxiety-like behaviour in mice and humans.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Mar;29(3):660-670. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02359-7. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38228888 Free PMC article.
-
The mood stabilizers lithium and valproate selectively activate the promoter IV of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neurons.Mol Psychiatry. 2009 Jan;14(1):51-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002099. Epub 2007 Oct 9. Mol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 17925795
-
Effect of childhood maltreatment and brain-derived neurotrophic factor on brain morphology.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016 Nov;11(11):1841-1852. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsw086. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27405617 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism on cognition in Bipolar Disorder: A review: Special Section on "Translational and Neuroscience Studies in Affective Disorders" Section Editor, Maria Nobile MD, PhD. This Section of JAD focuses on the relevance of translational and neuroscience studies in providing a better understanding of the neural basis of affective disorders. The main aim is to briefly summaries relevant research findings in clinical neuroscience with particular regards to specific innovative topics in mood and anxiety disorders.J Affect Disord. 2019 Jan 15;243:552-558. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.07.054. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Affect Disord. 2019. PMID: 30078664 Review.
-
A comprehensive review of genetic and epigenetic mechanisms that regulate BDNF expression and function with relevance to major depressive disorder.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2018 Mar;177(2):143-167. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32616. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29243873 Review.
Cited by
-
GWAS of stool frequency provides insights into gastrointestinal motility and irritable bowel syndrome.Cell Genom. 2021 Dec 8;1(3):None. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2021.100069. Cell Genom. 2021. PMID: 34957435 Free PMC article.
-
Association of HHV‑6 reactivation and SLC6A3 (C>T, rs40184), BDNF (C>T, rs6265), and JARID2 (G>A, rs9383046) single nucleotide polymorphisms in depression.Biomed Rep. 2024 Oct 3;21(6):181. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1869. eCollection 2024 Dec. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 39420919 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF promoter methylation and genetic variation in late-life depression.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Aug 18;5(8):e619. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.114. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26285129 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Functions of Multiple Bdnf Transcripts Driven by Distinct Bdnf Promoters.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 6;13(4):655. doi: 10.3390/biom13040655. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An ancient polymorphic regulatory region within the BDNF gene associated with obesity modulates anxiety-like behaviour in mice and humans.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Mar;29(3):660-670. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02359-7. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38228888 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rossi C., Angelucci A., Costantin L., Braschi C., Mazzantini M., Babbini F. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is required for the enhancement of hippocampal neurogenesis following environmental enrichment. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;24:1850–1856. - PubMed
-
- Tolwani R.J., Buckmaster P.S., Varma S., Cosgaya J.M., Wu Y., Suri C., Shooter E.M. BDNF overexpression increases dendrite complexity in hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neuroscience. 2002;114:795–805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

