Pretreatment with nomifensine or nomifensine analogue 4-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline augments methamphetamine-induced stereotypical behavior in mice
- PMID: 22265332
- PMCID: PMC4093904
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.12.043
Pretreatment with nomifensine or nomifensine analogue 4-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline augments methamphetamine-induced stereotypical behavior in mice
Abstract
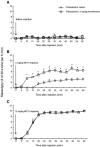
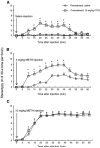
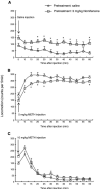
Nomifensine is a dopamine/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Nomifensine and some of its structural analogues produce behavioral effects indicative of indirect dopaminergic agonist properties, such as hyperlocomotion. By contrast, the deaminated and demethylated nomifensine analogue 4-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (PTIQ) is reported to have amphetamine-antagonistic properties, as demonstrated by inhibition of methamphetamine (METH)-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and METH-induced hyperlocomotion in rats. In the present study, we examined the effect of PTIQ (10mg/kg, i.p.) and nomifensine (3mg/kg, i.p.) on METH (5 or 10mg/kg, i.p.)-induced stereotypical behavior in mice in order to determine whether PTIQ and nomifensine inhibit and augment, respectively, METH-induced stereotypical behavior. Unexpectedly, our observations demonstrated that both PTIQ and nomifensine significantly augmented METH-induced stereotypical behavior and locomotion in mice. This augmentation is likely the result of additive effects on dopaminergic function by METH in combination with PTIQ or nomifensine. These results suggest that, contrary to some reports, PTIQ may display dopaminergic agonist properties in mice.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
4-Phenyltetrahydroisoquinoline, but not nomifensine or cocaine, inhibits methamphetamine-induced dopamine release.Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 10;240(1):51-6. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90544-r. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8405121
-
Inhibitory effect of 4-phenyltetrahydroisoquinoline on locomotion and dopamine release induced by micro-injection of methamphetamine into the nucleus accumbens of the rat.Neuropharmacology. 1993 Aug;32(8):761-6. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90184-5. Neuropharmacology. 1993. PMID: 8413840
-
Effect of 4-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline on ambulation induced by injection of methamphetamine into the nucleus accumbens in rats.Neuropharmacology. 1993 Mar;32(3):243-8. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90107-e. Neuropharmacology. 1993. PMID: 8474620
-
Metoprine, a histamine N-methyltransferase inhibitor, attenuates methamphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion via activation of histaminergic neurotransmission in mice.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021 Oct;209:173257. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2021.173257. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021. PMID: 34418452
-
Protective effects of cholecystokinin-8 on methamphetamine-induced behavioral changes and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Apr 15;283:87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.01.028. Epub 2015 Jan 25. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25629941
Cited by
-
Brain Histamine N-Methyltransferase As a Possible Target of Treatment for Methamphetamine Overdose.Drug Target Insights. 2016 Mar 2;10:1-7. doi: 10.4137/DTI.S38342. eCollection 2016. Drug Target Insights. 2016. PMID: 26966348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pretreatment or Posttreatment with Aripiprazole Attenuates Methamphetamine-induced Stereotyped Behavior in Mice.J Exp Neurosci. 2015 Sep 10;9(Suppl 1):1-10. doi: 10.4137/JEN.S27733. eCollection 2015. J Exp Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26525833 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium for schizophrenia: supporting evidence from a 12-year, nationwide health insurance database and from Akt1-deficient mouse and cellular models.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 20;10(1):647. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57340-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31959776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Khatib IMH, Dökmeci I, Fujiwara M. Differential role of nucleus accumbens and caudate-putamen in mediating the effect of nomifensine and methamphetamine on ambulation and rearing of rats in the open-field test. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1995;67:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Bournerias F, Nabibi B. Nomifensine-induced immune haemolytic anaemia and impaired renal function. Lancet. 1979;2:95–96. - PubMed
-
- Brogden RN, Heel RC, Speight TM, Avery GS. Nomifensine: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficiency in depressive illness. Drugs. 1979;18:1–24. - PubMed
-
- Church WH, Justice JB, Jr., Byrd LD. Extracellular dopamine in rat striatum following uptake inhibition by cocaine, nomifensine and benztropine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1987;139:345–348. - PubMed
-
- Costall B, Kelly DM, Naylor RJ. Nomifensine: a potent dopaminergic agonist of antiparkinson potential. Psychopharmacologia. 1975;41:153–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

