Foxa1 and Foxa2 are essential for sexual dimorphism in liver cancer
- PMID: 22265403
- PMCID: PMC3266536
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.026
Foxa1 and Foxa2 are essential for sexual dimorphism in liver cancer
Abstract
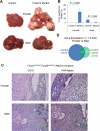
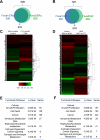
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is sexually dimorphic in both rodents and humans, with significantly higher incidence in males, an effect that is dependent on sex hormones. The molecular mechanisms by which estrogens prevent and androgens promote liver cancer remain unclear. Here, we discover that sexually dimorphic HCC is completely reversed in Foxa1- and Foxa2-deficient mice after diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Coregulation of target genes by Foxa1/a2 and either the estrogen receptor (ERα) or the androgen receptor (AR) was increased during hepatocarcinogenesis in normal female or male mice, respectively, but was lost in Foxa1/2-deficient mice. Thus, both estrogen-dependent resistance to and androgen-mediated facilitation of HCC depend on Foxa1/2. Strikingly, single nucleotide polymorphisms at FOXA2 binding sites reduce binding of both FOXA2 and ERα to their targets in human liver and correlate with HCC development in women. Thus, Foxa factors and their targets are central for the sexual dimorphism of HCC.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Why men are at higher risk for hepatocellular carcinoma?J Hepatol. 2012 Aug;57(2):453-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.004. Epub 2012 Mar 13. J Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22425699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carroll JS, Liu XS, Brodsky AS, Li W, Meyer CA, Szary AJ, Eeckhoute J, Shao W, Hestermann EV, Geistlinger TR, et al. Chromosome-wide mapping of estrogen receptor binding reveals long-range regulation requiring the forkhead protein FoxA1. Cell. 2005;122:33–43. - PubMed
-
- Di Maio M, De Maio E, Morabito A, D'Aniello R, De Feo G, Gallo C, Perrone F. Hormonal treatment of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1089:252–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

