Gene regulatory logic for reading the Sonic Hedgehog signaling gradient in the vertebrate neural tube
- PMID: 22265416
- PMCID: PMC3267043
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.047
Gene regulatory logic for reading the Sonic Hedgehog signaling gradient in the vertebrate neural tube
Abstract
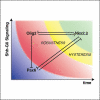
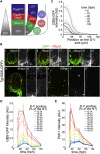
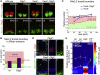
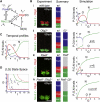
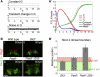
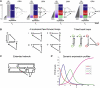
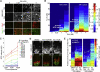
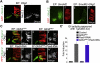
Secreted signals, known as morphogens, provide the positional information that organizes gene expression and cellular differentiation in many developing tissues. In the vertebrate neural tube, Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) acts as a morphogen to control the pattern of neuronal subtype specification. Using an in vivo reporter of Shh signaling, mouse genetics, and systems modeling, we show that a spatially and temporally changing gradient of Shh signaling is interpreted by the regulatory logic of a downstream transcriptional network. The design of the network, which links three transcription factors to Shh signaling, is responsible for differential spatial and temporal gene expression. In addition, the network renders cells insensitive to fluctuations in signaling and confers hysteresis--memory of the signal. Our findings reveal that morphogen interpretation is an emergent property of the architecture of a transcriptional network that provides robustness and reliability to tissue patterning.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Ahn S., Joyner A.L. Dynamic changes in the response of cells to positive hedgehog signaling during mouse limb patterning. Cell. 2004;118:505–516. - PubMed
-
- Alon U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007;8:450–461. - PubMed
-
- Bollenbach T., Pantazis P., Kicheva A., Bökel C., González-Gaitán M., Jülicher F. Precision of the Dpp gradient. Development. 2008;135:1137–1146. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J., Sussel L., Serup P., Hartigan-O'Connor D., Jessell T.M., Rubenstein J.L., Ericson J. Homeobox gene Nkx2.2 and specification of neuronal identity by graded Sonic hedgehog signalling. Nature. 1999;398:622–627. - PubMed
Supplemental References
-
- Buscher, D., Grotewold, L., and Ruther, U. (1998). The XtJ allele generates a Gli3 fusion transcript. Mamm. Genome 9, 676–678. - PubMed
-
- Chung, J.H., Whiteley, M., and Felsenfeld, G. (1993). A 5′ element of the chicken beta-globin domain serves as an insulator in human erythroid cells and protects against position effect in Drosophila. Cell 74, 505–514. - PubMed
-
- Das, R.M., Van Hateren, N.J., Howell, G.R., Farrell, E.R., Bangs, F.K., Porteous, V.C., Manning, E.M., McGrew, M.J., Ohyama, K., Sacco, M.A., et al. (2006). A robust system for RNA interference in the chicken using a modified microRNA operon. Dev. Biol. 294, 554–563. - PubMed
-
- Dessaud, E., Yang, L.L., Hill, K., Cox, B., Ulloa, F., Ribeiro, A., Mynett, A., Novitch, B.G., and Briscoe, J. (2007). Interpretation of the sonic hedgehog morphogen gradient by a temporal adaptation mechanism. Nature 450, 717–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

