Cooperative interactions between hippocampal and striatal systems support flexible navigation
- PMID: 22266411
- PMCID: PMC3303973
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.046
Cooperative interactions between hippocampal and striatal systems support flexible navigation
Abstract
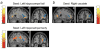
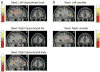
Research in animals and humans has demonstrated that the hippocampus is critical for retrieving distinct representations of overlapping sequences of information. There is recent evidence that the caudate nucleus and orbitofrontal cortex are also involved in disambiguation of overlapping spatial representations. The hippocampus and caudate are functionally distinct regions, but both have anatomical links with the orbitofrontal cortex. The present study used an fMRI-based functional connectivity analysis in humans to examine the functional relationship between the hippocampus, caudate, and orbitofrontal cortex when participants use contextual information to navigate well-learned spatial routes which share common elements. Participants were trained outside the scanner to navigate virtual mazes from a first-person perspective. Overlapping condition mazes began and ended at distinct locations, but converged in the middle to share some hallways with another maze. Non-overlapping condition mazes did not share any hallways with any other maze. Successful navigation through the overlapping hallways required contextual information identifying the current navigational route to guide the appropriate response for a given trial. Results revealed greater functional connectivity between the hippocampus, caudate, and orbitofrontal cortex for overlapping mazes compared to non-overlapping mazes. The current findings suggest that the hippocampus and caudate interact with prefrontal structures cooperatively for successful contextually dependent navigation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Which way was I going? Contextual retrieval supports the disambiguation of well learned overlapping navigational routes.J Neurosci. 2010 May 26;30(21):7414-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6021-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20505108 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Contributions of medial temporal lobe and striatal memory systems to learning and retrieving overlapping spatial memories.Cereb Cortex. 2014 Jul;24(7):1906-22. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bht041. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Cereb Cortex. 2014. PMID: 23448868 Free PMC article.
-
A high-resolution study of hippocampal and medial temporal lobe correlates of spatial context and prospective overlapping route memory.Hippocampus. 2014 Jul;24(7):819-39. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22273. Epub 2014 Apr 17. Hippocampus. 2014. PMID: 24659134 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating hippocampus and striatum in decision-making.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007 Dec;17(6):692-7. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.01.003. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 18313289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampus and striatum: dynamics and interaction during acquisition and sleep-related motor sequence memory consolidation.Hippocampus. 2013 Nov;23(11):985-1004. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22183. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 23929594 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for a gradient within the medial temporal lobes for flexible retrieval under hierarchical task rules.Hippocampus. 2021 Sep;31(9):1003-1019. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23365. Epub 2021 May 26. Hippocampus. 2021. PMID: 34038011 Free PMC article.
-
Interindividual differences in memory system local field potential activity predict behavioral strategy on a dual-solution T-maze.Hippocampus. 2020 Dec;30(12):1313-1326. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23258. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Hippocampus. 2020. PMID: 32894595 Free PMC article.
-
NLM-HS: Navigation Learning Model Based on a Hippocampal-Striatal Circuit for Explaining Navigation Mechanisms in Animal Brains.Brain Sci. 2021 Jun 17;11(6):803. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11060803. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34204482 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual water maze learning in human increases functional connectivity between posterior hippocampus and dorsal caudate.Hum Brain Mapp. 2015 Apr;36(4):1265-77. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22700. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015. PMID: 25418860 Free PMC article.
-
Human hippocampal processing of environmental novelty during spatial navigation.Hippocampus. 2014 Jul;24(7):740-50. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22264. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Hippocampus. 2014. PMID: 24550152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander GE, DeLong MR, Strick PL. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Ann Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:357–381. - PubMed
-
- Andersson JL, Hutton C, Ashburner J, Turner R, Friston K. Modeling geometric deformations in EPI time series. Neuroimage. 2001;13:903–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

