Splenocyte apoptosis and autophagy is mediated by interferon regulatory factor 1 during murine endotoxemia
- PMID: 22266972
- PMCID: PMC3328635
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318249cfa2
Splenocyte apoptosis and autophagy is mediated by interferon regulatory factor 1 during murine endotoxemia
Abstract
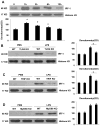
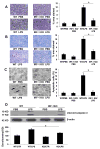
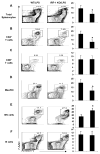
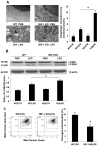
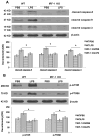
Sepsis-induced lymphocyte and dendritic cell apoptosis contributes to immunosuppression, which results in an inability to eradicate the primary infection as well as a propensity to acquire new, secondary infections. Another cellular process, autophagy, is also activated in immune cells and plays a protective role. In the present study, we demonstrate that interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) regulates both immune cell apoptosis and autophagy in a murine endotoxemia model. Interferon regulatory factor 1 is activated at an early phase through a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent, myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88-independent manner in splenocytes. Furthermore, IRF-1 knockout (KO) mice are protected from a lethal endotoxemia model. This protection is associated with decreased apoptosis and increased autophagy in splenocytes. Interferon regulatory factor 1 KO mice experience decreased apoptotic cell loss, especially in CD4⁺ T lymphocytes and myeloid antigen-presenting cells. Meanwhile, IRF-1 KO mice demonstrate increased autophagy and improved mitochondrial integrity. This increased autophagy in KO mice is attributable, at least in part, to deactivation of mammalian target of rapamycin/P70S6 signaling--a main negative regulator of autophagy. Therefore, we propose a novel role for IRF-1 in regulating both apoptosis and autophagy in splenocytes in the setting of endotoxemia with IRF-1 promoting apoptosis and inhibiting autophagy.
Figures
References
-
- Aneja R, Fink MP. Promising therapeutic agents for sepsis. Trends Microbiol. 2007;15(1):31–7. - PubMed
-
- Park BS, Song DH, Kim HM, Choi BS, Lee H, Lee JO. The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature. 2009;458(7242):1191–5. - PubMed
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD, Tinsley KW, Cobb JP, Matuschak GM, Buchman TG, Karl IE. Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 1999;27(7):1230–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

