Metabolomics implicates altered sphingolipids in chronic pain of neuropathic origin
- PMID: 22267119
- PMCID: PMC3567618
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.767
Metabolomics implicates altered sphingolipids in chronic pain of neuropathic origin
Abstract
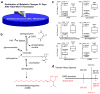
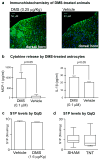
Neuropathic pain is a debilitating condition for which the development of effective treatments has been limited by an incomplete understanding of its chemical basis. We show by using untargeted metabolomics that sphingomyelin-ceramide metabolism is altered in the dorsal horn of rats with neuropathic pain and that the upregulated, endogenous metabolite N,N-dimethylsphingosine induces mechanical hypersensitivity in vivo. These results demonstrate the utility of metabolomics to implicate unexplored biochemical pathways in disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Metabolomics: Gaining insight into pain.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Mar 1;11(3):188-9. doi: 10.1038/nrd3685. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22378263 No abstract available.
References
-
- Torrance N, Smith BH, Bennett MI, Lee AJ. The epidemiology of chronic pain of predominantly neuropathic origin. Results from a general population survey. J Pain. 2006;7:281–9. - PubMed
-
- Warfield CA, Fausett HJ. Manual of Pain Management. In: Warfield CA, Fausett HJ, editors. Manual of Pain Management. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2002.
-
- Woolf CJ, Mannion RJ. Neuropathic pain: aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet. 1999;353:1959–64. - PubMed
-
- Sung YJ, Ambron RT. Pathways that elicit long-term changes in gene expression in nociceptive neurons following nerve injury: contributions to neuropathic pain. Neurol Res. 2004;26:195–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R24 EY017540-04/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062261/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025774/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA026146/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AG038036/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA026146-02/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS068015/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32NS068015/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AG0 038036/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RR025774/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS041219/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 EY017540/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

