Meta-analyses identify 13 loci associated with age at menopause and highlight DNA repair and immune pathways
- PMID: 22267201
- PMCID: PMC3288642
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.1051
Meta-analyses identify 13 loci associated with age at menopause and highlight DNA repair and immune pathways
Abstract
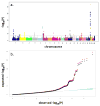
To newly identify loci for age at natural menopause, we carried out a meta-analysis of 22 genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in 38,968 women of European descent, with replication in up to 14,435 women. In addition to four known loci, we identified 13 loci newly associated with age at natural menopause (at P < 5 × 10(-8)). Candidate genes located at these newly associated loci include genes implicated in DNA repair (EXO1, HELQ, UIMC1, FAM175A, FANCI, TLK1, POLG and PRIM1) and immune function (IL11, NLRP11 and PRRC2A (also known as BAT2)). Gene-set enrichment pathway analyses using the full GWAS data set identified exoDNase, NF-κB signaling and mitochondrial dysfunction as biological processes related to timing of menopause.
Conflict of interest statement
Some of the authors declare competing financial interests: details accompany the full-text HTML version of the paper
Figures
References
-
- Burger HG. The menopausal transition. Baillieres Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1996;10:347–59. - PubMed
-
- Broekmans FJ, Soules MR, Fauser BC. Ovarian aging: mechanisms and clinical consequences. Endocr Rev. 2009;30:465–93. - PubMed
-
- te Velde ER, Pearson PL. The variability of female reproductive ageing. Hum Reprod Update. 2002;8:141–54. - PubMed
-
- te Velde ER, Dorland M, Broekmans FJ. Age at menopause as a marker of reproductive ageing. Maturitas. 1998;30:119–25. - PubMed
-
- Murabito JM, Yang Q, Fox C, Wilson PW, Cupples LA. Heritability of age at natural menopause in the Framingham Heart Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:3427–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CZB/4/710/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- N01 HC085086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL064278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR041398/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG050002/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG032598/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0700704/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA040356/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC035129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R69/0208/DMT_/The Dunhill Medical Trust/United Kingdom
- K05 AA017688/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG012100/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072488/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127592696/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 AG012109/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HL072515/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U127592696/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous