Passive mechanical properties of rat abdominal wall muscles suggest an important role of the extracellular connective tissue matrix
- PMID: 22267257
- PMCID: PMC3337947
- DOI: 10.1002/jor.22068
Passive mechanical properties of rat abdominal wall muscles suggest an important role of the extracellular connective tissue matrix
Abstract
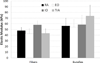
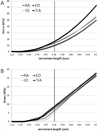
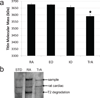
Abdominal wall muscles have a unique morphology suggesting a complex role in generating and transferring force to the spinal column. Studying passive mechanical properties of these muscles may provide insights into their ability to transfer force among structures. Biopsies from rectus abdominis (RA), external oblique (EO), internal oblique (IO), and transverse abdominis (TrA) were harvested from male Sprague-Dawley rats, and single muscle fibers and fiber bundles (4-8 fibers ensheathed in their connective tissue matrix) were isolated and mechanically stretched in a passive state. Slack sarcomere lengths were measured and elastic moduli were calculated from stress-strain data. Titin molecular mass was also measured from single muscle fibers. No significant differences were found among the four abdominal wall muscles in terms of slack sarcomere length or elastic modulus. Interestingly, across all four muscles, slack sarcomere lengths were quite long in individual muscle fibers (>2.4 µm), and demonstrated a significantly longer slack length in comparison to fiber bundles (p < 0.0001). Also, the extracellular connective tissue matrix provided a stiffening effect and enhanced the resistance to lengthening at long muscle lengths. Titin molecular mass was significantly less in TrA compared to each of the other three muscles (p < 0.0009), but this difference did not correspond to hypothesized differences in stiffness.
Copyright © 2012 Orthopaedic Research Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effect of vertebral level on biomechanical properties of the lumbar paraspinal muscles in a rat model.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021 Jun;118:104446. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.104446. Epub 2021 Mar 15. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021. PMID: 33780860
-
Nonuniform elasticity of titin in cardiac myocytes: a study using immunoelectron microscopy and cellular mechanics.Biophys J. 1996 Jan;70(1):430-42. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79586-3. Biophys J. 1996. PMID: 8770219 Free PMC article.
-
Titin elasticity and mechanism of passive force development in rat cardiac myocytes probed by thin-filament extraction.Biophys J. 1997 Oct;73(4):2043-53. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78234-1. Biophys J. 1997. PMID: 9336199 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanisms of the residual force enhancement after stretch of skeletal muscle: non-uniformity in half-sarcomeres and stiffness of titin.Proc Biol Sci. 2012 Jul 22;279(1739):2705-13. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2012.0467. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Proc Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22535786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of titin in the structure and elasticity of the sarcomere.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:612482. doi: 10.1155/2010/612482. Epub 2010 Jun 21. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20625501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ergojump evaluation of the explosive strength in volleyball athletes pre- and post-fascial treatment.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Aug;18(2):1470-1476. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7628. Epub 2019 May 29. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31384337 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of High-Intensity Ultrasound on Strength of Surgical Mesh When Treating Biofilm Infections.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2019 Jan;66(1):38-44. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2018.2881358. Epub 2018 Nov 14. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2019. PMID: 30442604 Free PMC article.
-
How does tissue preparation affect skeletal muscle transverse isotropy?J Biomech. 2016 Sep 6;49(13):3056-3060. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2016.06.034. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Biomech. 2016. PMID: 27425557 Free PMC article.
-
Non-linear Scaling of Passive Mechanical Properties in Fibers, Bundles, Fascicles and Whole Rabbit Muscles.Front Physiol. 2020 Mar 20;11:211. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00211. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32265730 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Function relationships in the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix.J Biomech. 2023 May;152:111593. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2023.111593. Epub 2023 Apr 17. J Biomech. 2023. PMID: 37099932 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brown SHM, McGill SM. A comparison of ultrasound and electromyography measures of force and activation to examine the mechanics of abdominal wall contraction. Clin Biomech. 2010;25:115–123. - PubMed
-
- Hwang W, Carvalho JC, Tarlovsky I, Boriek AM. Passive mechanics of canine internal abdominal wall muscles. J Appl Physiol. 2005;98:1829–1835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

