SlyA regulates type III secretion system (T3SS) genes in parallel with the T3SS master regulator HrpL in Dickeya dadantii 3937
- PMID: 22267675
- PMCID: PMC3318817
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.07021-11
SlyA regulates type III secretion system (T3SS) genes in parallel with the T3SS master regulator HrpL in Dickeya dadantii 3937
Abstract
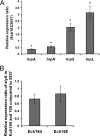
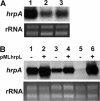
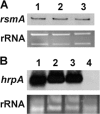
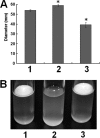
The hypersensitive response and pathogenicity (hrp) genes of Dickeya dadantii 3937 encode a type III secretion system (T3SS) which is essential for its full virulence. Previous studies of the T3SS regulation in D. dadantii 3937 revealed that the expression of the hrp genes is regulated by a master regulator, HrpL, through the HrpX-HrpY-HrpS-HrpL and GacS-GacA-rsmB-RsmA pathways. In this work, we identified a novel regulator of the SlyA/MarR family, SlyA, which regulates hrp genes of the HrpL regulon in parallel with HrpL in D. dadantii. SlyA regulates the T3SS in a two-tier manner. It negatively regulates the expression of hrpL by downregulating hrpS and upregulating rsmA. Interestingly, concomitant with its downregulation of the hrpL, SlyA positively regulates the expression of hrpA and hrpN, two hrp genes located in the HrpL regulon. In contrast to Pectobacterium carotovorum, the expression of slyA is not controlled by ExpR and ExpI in D. dadantii 3937. We further show that SlyA is involved in controlling swimming motility and pellicle formation in D. dadantii 3937.
Figures
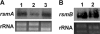
Similar articles
-
The Response regulator HrpY of Dickeya dadantii 3937 regulates virulence genes not linked to the hrp cluster.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008 Mar;21(3):304-14. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-3-0304. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008. PMID: 18257680
-
Dynamic regulation of GacA in type III secretion, pectinase gene expression, pellicle formation, and pathogenicity of Dickeya dadantii (Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937).Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008 Jan;21(1):133-42. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-1-0133. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008. PMID: 18052890
-
Type III secretion system genes of Dickeya dadantii 3937 are induced by plant phenolic acids.PLoS One. 2008 Aug 13;3(8):e2973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002973. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18698421 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of virulence by members of the MarR/SlyA family.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006 Apr;9(2):153-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.02.003. Epub 2006 Mar 10. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16529980 Review.
-
Innovation and Application of the Type III Secretion System Inhibitors in Plant Pathogenic Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2020 Dec 9;8(12):1956. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8121956. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33317075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Five Plant Natural Products Are Potential Type III Secretion System Inhibitors to Effectively Control Soft-Rot Disease Caused by Dickeya.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 22;13:839025. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.839025. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35273588 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-species interactions between two bacterial flower commensals and a floral pathogen reduce disease incidence and alter pathogen activity.mBio. 2024 Mar 13;15(3):e0021324. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00213-24. Epub 2024 Feb 20. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38376185 Free PMC article.
-
The post-transcriptional regulator rsmA/csrA activates T3SS by stabilizing the 5' UTR of hrpG, the master regulator of hrp/hrc genes, in Xanthomonas.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Feb 27;10(2):e1003945. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003945. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24586158 Free PMC article.
-
OhrR is a central transcriptional regulator of virulence in Dickeya zeae.Mol Plant Pathol. 2022 Jan;23(1):45-59. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13141. Epub 2021 Oct 24. Mol Plant Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34693617 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-Adapted Bacteria Isolated From Wastewaters Produce Biofilms by Expressing Proteinaceous Curli Fimbriae and Cellulose Nanofibers.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jun 25;9:1334. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01334. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29988579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alekshun MN, Kim YS, Levy SB. 2000. Mutational analysis of MarR, the negative regulator of marRAB expression in Escherichia coli, suggests the presence of two regions required for DNA binding. Mol. Microbiol. 35:1394–1404 - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee A, Cui Y, Liu Y, Dumenyo CK, Chatterjee AK. 1995. Inactivation of rsmA leads to overproduction of extracellular pectinases, cellulases, and proteases in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora in the absence of the starvation/cell density-sensing signal, N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61:1959–1967 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cui Y, Chatterjee A, Liu Y, Dumenyo CK, Chatterjee AK. 1995. Identification of a global repressor gene, rsmA, of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora that controls extracellular enzymes, N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone, and pathogenicity in soft-rotting Erwinia spp. J. Bacteriol. 177:5108–5115 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cui Y, Chatterjee A, Yang H, Chatterjee AK. 2008. Regulatory network controlling extracellular proteins in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora: FlhDC, the master regulator of flagellar genes, activates rsmB regulatory RNA production by affecting gacA and hexA (lrhA) expression. J. Bacteriol. 190:4610–4623 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

