Nebulized liposomal gadobenate dimeglumine contrast formulation for magnetic resonance imaging of larynx and trachea
- PMID: 22267923
- PMCID: PMC3260032
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S25546
Nebulized liposomal gadobenate dimeglumine contrast formulation for magnetic resonance imaging of larynx and trachea
Abstract
Background: To develop a lipid-stabilized contrast formulation containing gadobenate dimeglumine for clear visualization of the mucosal surfaces of the larynx and trachea for early diagnosis of disease by magnetic resonance imaging.
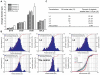
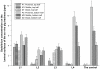
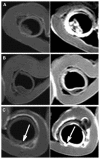
Methods: The contrast formulation was prepared by loading gadobenate dimeglumine into egg phosphotidylcholine, cholesterol, and sterylamine nanoliposomes using the dehydration-rehydration method. The liposomal contrast formulation was ultrasonically nebulized, and the deposition and coating pattern on explanted pig laryngeal and tracheal segments was examined by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. The sizes of the nebulized droplets were characterized by photon correlation spectroscopy. The contrast-enhanced mucosal surface images of the larynx and trachea were obtained in a 3.0T magnetic resonance scanner using a T1-weighted spectral presaturation inversion recovery sequence.
Results: Various cationic liposome formulations were compared for their stabilization effects on the droplets containing gadobenate dimeglumine. The liposomes composed of egg phosphotidylcholine, cholesterol, and sterylamine in a molar ratio of 1:1:1 were found to enable the most efficient nebulization and the resulting droplet sizes were narrowly distributed. They also resulted in the most even coating on the laryngeal and tracheal lumen surfaces and produced significant contrast enhancement along the mucosal surface. Such contrast enhancement could help clearer visualization of several disease states, such as intraluminal protrusions, submucosal nodules, and craters.
Conclusion: This lipid-stabilized magnetic resonance imaging contrast formulation may be useful for improving mucosal surface visualization and early diagnosis of disease originating in the mucosal surfaces of the larynx and trachea.
Keywords: gadolinium; lipid; magnetic resonance imaging; mucoadhesion; nebulization; upper airway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gadobenate dimeglumine 0.5 M solution for injection (MultiHance) pharmaceutical formulation and physicochemical properties of a new magnetic resonance imaging contrast medium.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999 Nov;23 Suppl 1:S161-8. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199911001-00021. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999. PMID: 10608412 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution in animals of gadobenate ion, the magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancing component of gadobenate dimeglumine 0.5 M solution for injection (MultiHance).J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999 Nov;23 Suppl 1:S181-94. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199911001-00023. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999. PMID: 10608414
-
Low dose gadobenate dimeglumine for imaging of chronic myocardial infarction in comparison with standard dose gadopentetate dimeglumine.Invest Radiol. 2009 Feb;44(2):95-104. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181911eab. Invest Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19077911 Clinical Trial.
-
Signal intensity change on unenhanced T1-weighted images in dentate nucleus following gadobenate dimeglumine in patients with and without previous multiple administrations of gadodiamide.Eur Radiol. 2016 Nov;26(11):4080-4088. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4269-7. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Eur Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26911888
-
Gadobenate dimeglumine 0.5 M solution for injection (MultiHance) as contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging of the liver: mechanistic studies in animals.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999 Nov;23 Suppl 1:S169-79. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199911001-00022. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999. PMID: 10608413 Review.
References
-
- Becker M, Burkhardt K, Dulguerov P, Allal A. Imaging of the larynx and hypopharynx. Eur J Radiol. 2008;66(3):460–479. - PubMed
-
- Hermans R. Staging of laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer: value of imaging studies. Eur Radiol. 2006;16(11):2386–2400. - PubMed
-
- Mathisen D. Primary tracheal tumor management. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 1999;8(2):307. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

