Lipodystrophy in HIV patients: its challenges and management approaches
- PMID: 22267946
- PMCID: PMC3257972
- DOI: 10.2147/HIV.S14562
Lipodystrophy in HIV patients: its challenges and management approaches
Abstract
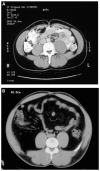
HIV-associated lipodystrophy is a term used to describe a constellation of body composition (lipoatrophy and lipohypertrophy) and metabolic (dyslipidemia and insulin resistance) alterations that accompany highly active antiretroviral therapy. These changes, which resemble metabolic syndrome, have been associated with a variety of adverse outcomes including accelerated cardiovascular disease. The body composition and metabolic changes appear to cluster in HIV infection, although they are distinct alterations and do not necessarily coexist. Epidemiological studies have demonstrated multiple pathogenic influences associated with host, disease, and treatment-related factors. The adverse treatment effects were more prominent in early regimens; continued drug development has led to the application of metabolically safer regimens with equal or greater potency than the regimens being replaced. Disease-related factors include HIV infection as well as inflammation, immune activation, and immune depletion. The body composition changes promote anxiety and depression in patients and may affect treatment adherence. Treatment of dyslipidemia and alterations in glucose metabolism is the same as in non-HIV-infected individuals. Lipoatrophy is managed by strategic choice of antivirals or by antiviral switching, and in some cases by plastic/reconstructive surgery. Lipohypertrophy has been managed mainly by lifestyle modification, ie, a hypocaloric diet and increased exercise. A growth hormone releasing factor, which reduces central fat, has recently become available for clinical use.
Keywords: body composition; dyslipidemia; insulin resistance; lipoatrophy; lipohypertrophy.
Figures

References
-
- Garg A. Acquired and inherited lipodystrophies. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1220–1234. - PubMed
-
- Safrin S, Grunfeld C. Fat distribution and metabolic changes in patients with HIV infection. AIDS. 1999;13:2493–2505. - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Baker RK, Moorman AC, et al. Mortality in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era: changing causes of death and disease in the HIV outpatient study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1998;43:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Carr A, Samaras K, Burton S, et al. A syndrome of peripheral lipodystrophy, hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance in patients receiving protease inhibitors. AIDS. 1998;12:F51–F58. - PubMed
-
- Podzamczer D, Ferrer E, Martínez E, et al. How much fat loss is needed for lipoatrophy to become clinically evident. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2009;25:563–567. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

