An Improved Element Design for 64-Channel Planar Imaging
- PMID: 22267961
- PMCID: PMC3259609
- DOI: 10.1002/cmr.b.20203
An Improved Element Design for 64-Channel Planar Imaging
Abstract
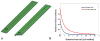
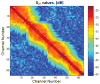
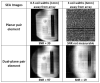
Investigation of highly accelerated MRI has developed into a lively corner in the hardware and methodology arena in recent years. At the extreme of (one-dimensional) acceleration, our group introduced Single Echo Acquisition (SEA) imaging, in which the need to phase encode a 64×N(readout) image is eliminated and replaced with the well-localized spatial information obtained from an array of 64 very narrow, long, parallel coils. The narrow coil width (2mm) that facilitates this is accompanied by a concomitant constraint on the useful imaging depth. This note describes a 64-element planar array, constructed within the same 8×13cm total footprint as the original SEA array, still enabling full acceleration in one dimension, but with an element design modified to increase the imaging depth. This was accomplished by lowering the outer conducting legs of the planar pair with respect to the center conductor and adding a geometric decoupling configuration away from the imaging field of view. The element has been called a dual-plane pair in that the current carrying rungs in the imaging FOV function exactly as the planar pair, but are simply placed in two separate planes (sides of PCB in this case).
Figures
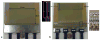

Similar articles
-
64-channel array coil for single echo acquisition magnetic resonance imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2005 Aug;54(2):386-92. doi: 10.1002/mrm.20568. Magn Reson Med. 2005. PMID: 16032696
-
Overcoming phase effects of voxel-sized coils in planar and cylindrical arrays.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2004;2004:1060-3. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2004.1403346. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2004. PMID: 17271865
-
Exploration of highly accelerated magnetic resonance elastography using high-density array coils.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017 Apr;7(2):195-204. doi: 10.21037/qims.2017.04.02. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017. PMID: 28516045 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Channel Transverse Fields Radiofrequency Coils for 1.5 T Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 23;24(7):2049. doi: 10.3390/s24072049. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38610261 Free PMC article.
-
An endovaginal MRI array with a forward-looking coil for advanced gynecological cancer brachytherapy procedures: Design and initial results.Med Phys. 2021 Nov;48(11):7283-7298. doi: 10.1002/mp.15228. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34520574 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A parallel imaging approach to wide-field MR microscopy.Magn Reson Med. 2012 Sep;68(3):850-6. doi: 10.1002/mrm.23258. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Magn Reson Med. 2012. PMID: 22139858 Free PMC article.
-
Massively parallel MRI detector arrays.J Magn Reson. 2013 Apr;229:75-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Magn Reson. 2013. PMID: 23453758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carlson JW. An Algorithm for NMR Imaging Reconstruction Based on Multiple RF Receiver Coils. Journal of Magnetic Resonance. 1987;74:376–380.
-
- Hutchinson M, Raff U. Fast MRI data acquisition using multiple detectors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1988;6(1):87–91. - PubMed
-
- Kwiat D, Einav S, Navon G. A decoupled coil detector array for fast image acquisition in magnetic resonance imaging. Medical Physics. 1991;18(2):251–265. - PubMed
-
- Sodickson DK. Spatial encoding using multiple RF coils: SMASH imaging and parallel MRI. In: Young IR, editor. Methods in Biomedical Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy. John Wiley & Sons; 2000. pp. 239–250.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
