Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans of the scalp with fibrosarcomatous degeneration and pulmonary metastasis
- PMID: 22267990
- PMCID: PMC3261608
- DOI: 10.4103/2156-7514.90482
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans of the scalp with fibrosarcomatous degeneration and pulmonary metastasis
Abstract
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a rare locally aggressive cutaneous tumor of intermediate malignancy. It is a slow-growing neoplasm with a marked propensity to recur after resection. Head and neck involvement is unusual and distant metastases are quite rare but tend to be more frequent in tumors that undergo fibrosarcomatous degeneration. We present the imaging and corresponding histopathology in a case of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans of the scalp demonstrating fibrosarcomatous degeneration and lung metastasis.
Keywords: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans; imaging characteristics; lung metastasis; scalp.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
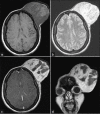

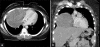
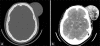

References
-
- Darier S, Ferrand M. Dermatofibrosarcomes progressives et ricidivantes on fibrosarcomes de la peau. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1924;5:545–62.
-
- Kransdorf MJ, Meis-Kindblom JM. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Radiologic appearance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162:391–4. - PubMed
-
- Torreggiani WC, Al-Ismail K, Munk PL, Nicolaou S, O'Connell JX, Knowling MA. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: MR Imaging Features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178:989–93. - PubMed
-
- Bowne WB, Antonescu CR, Leung DH, Katz SC, Hawkins WG, Woodruff JM, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A clinicopathologic analysis of patients treated and followed at a single institution. Cancer. 2000;88:2711–20. - PubMed
-
- Uematsu Y, Fukai J, Tamura M, Owai Y, Obayashi S, Nakai K, et al. Distant metastasis of dermatofibrosarcoma of the scalp. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2003;43:493–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

