Ionotropic glutamate receptors in the external lateral parabrachial nucleus participate in processing cardiac sympathoexcitatory reflexes
- PMID: 22268111
- PMCID: PMC3330787
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00984.2011
Ionotropic glutamate receptors in the external lateral parabrachial nucleus participate in processing cardiac sympathoexcitatory reflexes
Abstract
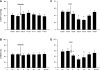
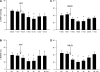
Stimulation of cardiac sympathetic afferents during myocardial ischemia with metabolites such as bradykinin (BK) evokes sympathoexcitatory reflex responses and activates neurons in the external lateral parabrachial nucleus (elPBN). The present study tested the hypothesis that this region in the pons processes sympathoexcitatory cardiac reflexes through an ionotropic glutamate receptor mechanism. The ischemic metabolite BK (0.1-1 μg) was injected into the pericardial space of anesthetized and bilaterally vagotomized or intact cats. Hemodynamic and renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) responses to repeated administration of BK before and after unilateral 50-nl microinjections of kynurenic acid (Kyn; 25 mM), 2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (AP5; 25 mM), and 2,3-dihydroxy-6-nitro-7-sulfamoyl-benzol(F)quinoxaline (NBQX; 10 mM) into the elPBN were recorded. Intrapericardial BK evoked significant increases in mean arterial pressure (MAP) and RSNA in seven vagotomized cats. After blockade of glutamate receptors with the nonselective glutamate receptor antagonist Kyn, the BK-evoked reflex increases in MAP (50 ± 6 vs. 29 ± 2 mmHg) and RSNA (59 ± 8.6 vs. 29 ± 4.7%, before vs. after) were significantly attenuated. The BK-evoked responses returned to pre-Kyn levels 85 min after the application of Kyn. Similarly, BK-evoked reflex responses were reversibly attenuated by blockade of glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors with AP5 (n = 5) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors with NBQX (n = 5). In contrast, we observed that the repetitive administration of BK evoked consistent reflex responses including MAP and RSNA before and after microinjection of 50 nl of the artificial cerebrospinal fluid vehicle into the elPBN in five animals. Microinjection of glutamate receptor antagonists into regions outside the elPBN did not alter BK-induced reflex responses. Microinjection of Kyn into the elPBN reversibly attenuated BK-induced reflex responses in four vagus intact animals. These data are the first to show that NMDA and AMPA ionotropic glutamate receptors in the elPBN play an important role in processing cardiac excitatory reflex responses.
Figures




References
-
- Anderson MK, Speck DF. Differential effects of excitatory amino acid receptor antagonism in the ventral respiratory group. Brain Res 829: 69–76, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Berman AL. The Brainstem of the Cat: a Cytoarchitectonic Atlas with Stereotaxic Coordinates. Madison, WI: Univ. of Wisconsin Press, 1968
-
- Chamberlin N, Saper C. Topographic organization of cardiovascular responses to electrical and glutamate microstimulation of the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 326: 245–262, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Craig AD. Distribution of brainstem projections from spinal lamina I neurons in the cat and the monkey. J Comp Neurol 361: 225–248, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

