Interstitial lung abnormalities and reduced exercise capacity
- PMID: 22268134
- PMCID: PMC3326424
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201109-1618OC
Interstitial lung abnormalities and reduced exercise capacity
Abstract
Rationale: The relationship between interstitial lung abnormalities (ILA) and exercise capacity has not been comprehensively evaluated.
Objectives: To assess the validity of the 6-minute walk test in subjects with ILA, and to examine the association between ILA and 6-minute walk distance (6MWD).
Methods: Spearman correlation coefficients were used to assess the strength of the relationships between 6MWD and relevant measures of dyspnea, health-related quality of life, and pulmonary function in a cohort of 2,416 people who smoke from the COPDGene study. Unadjusted and adjusted linear and logistic regression models were used to assess the strength of the association between ILA and 6MWD.
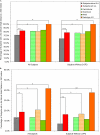
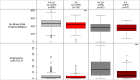
Measurements and main results: In all subjects, and in those with ILA, 6MWD in COPDGene was associated with relevant clinical and physiologic measures. The mean 6MWD in COPDGene subjects with ILA was 386 m (SD, 128 m), and 82% and 19% of subjects with ILA had 6MWDs less than or equal to 500 and 250 m, respectively. ILA was associated with a reduced 6MWD in univariate (-30 m; 95% confidence interval, -50 to -10; P = 0.004) and multivariate models (-19 m; 95% confidence interval, -33 to -5; P = 0.008). Compared with subjects without ILA, subjects with ILA had an 80% and 77% increase in their odds to have a walk distance limited to less than or equal to 500 and 250 m, respectively. Although these findings were dependent on ILA subtype, they were not limited to those with COPD.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that ILA is associated with measurable decrements in the 6MWD of people who smoke. Clinical trial registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT 00608764).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00608764.
Figures
Comment in
-
Secondary prevention of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: catching the horse still in the barn.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Apr 1;185(7):697-9. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201202-0222ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22467803 No abstract available.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:277–304 - PubMed
-
- du Bois RM, Weycker D, Albera C, Bradford WZ, Costabel U, Kartashov A, Lancaster L, Noble PW, Sahn SA, Szwarcberg J, et al. 6-minute walk test in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: test validation and minimal clinically important difference. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011;183:1231–1237 - PubMed
-
- Shah MR, Hasselblad V, Gheorghiade M, Adams KF, Jr, Swedberg K, Califf RM, O'Connor CM. Prognostic usefulness of the six-minute walk in patients with advanced congestive heart failure secondary to ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol 2001;88:987–993 - PubMed
-
- Cote CG, Casanova C, Marin JM, Lopez MV, Pinto-Plata V, de Oca MM, Dordelly LJ, Nekach H, Celli BR. Validation and comparison of reference equations for the 6-min walk distance test. Eur Respir J 2008;31:571–578 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007633/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32 HL007633-25/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21CA116271-2/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL092222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL087030/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA116271/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL089353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 CA157631/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111024/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

