Molecular cloning and characterization of PtrLAR3, a gene encoding leucoanthocyanidin reductase from Populus trichocarpa, and its constitutive expression enhances fungal resistance in transgenic plants
- PMID: 22268151
- PMCID: PMC3346219
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/err425
Molecular cloning and characterization of PtrLAR3, a gene encoding leucoanthocyanidin reductase from Populus trichocarpa, and its constitutive expression enhances fungal resistance in transgenic plants
Abstract
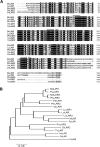
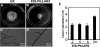
The flavonoid-derived proanthocyanidins (PAs) are one class of the major defence phenolics in poplar leaves. Transcriptional activation of PA biosynthetic genes, resulting in PA accumulation in leaves, was detected following infection by the fungal Marssonina brunnea f.sp. multigermtubi using digital gene expression analysis. In order to study PA biosynthesis and its induction by fungi, a putative leucoanthocyanidin reductase gene, PtrLAR3, was isolated from Populus trichocarpa. Sequence comparison of PtrLAR3 with other known leucoanthocyanidin reductase proteins revealed high amino acid sequence similarity. Semi-quantitative reverse-transcription (RT) PCR and quantitative real-time PCR analysis demonstrated that PtrLAR3 was expressed in various tissues and the highest level of expression was observed in roots. Overexpression of PtrLAR3 in Chinese white poplar (Populus tomentosa Carr.) led to a significant plant-wide increase in PA levels. In vitro assays showed that crude leaf extracts from 35S:PtrLAR3 transformants were able to inhibit significantly the hyphal growth of M. brunnea f.sp. multigermtubi compared to the extracts from control plants. The transgenic 35S:PtrLAR3 poplar plants displayed a significant (P < 0.05) reduction in their disease symptoms compared with the control. RT-PCR analysis showed that PtrLAR3 expression was up-regulated in all transformants. These results suggested that constitutive expression of endogenous PtrLAR3 could be exploited to improve resistance to fungal pathogens in poplar.
Figures





References
-
- Abrahams S, Lee E, Walker AR, Tanner GJ, Larkin PJ, Ashton AR. The Arabidopsis TDS4 gene encodes leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (LDOX) and is essential for proanthocyanidin synthesis and vacuole development. The Plant Journal. 2003;35:624–636. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Stohs SJ, Das DK, Ray SD, Kuszynski CA, Joshi SS, Pruess HG. Free radicals and grape seed proanthocyanidin extract: importance in human health and disease prevention. Toxicology. 2000;148:187–197. - PubMed

