Role of TGF-β and the tumor microenvironment during mammary tumorigenesis
- PMID: 22268294
- PMCID: PMC3723115
- DOI: 10.3727/105221611x13176664479322
Role of TGF-β and the tumor microenvironment during mammary tumorigenesis
Abstract
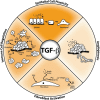
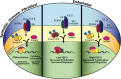
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) is a multifunctional cytokine that functions to inhibit mammary tumorigenesis by directly inducing mammary epithelial cells (MECs) to undergo cell cycle arrest or apoptosis, and to secrete a variety of cytokines, growth factors, and extracellular matrix proteins that maintain cell and tissue homeostasis. Genetic and epigenetic events that transpire during mammary tumorigenesis typically inactivate the tumor suppressing activities of TGF-beta and ultimately confer this cytokine with tumor promoting activities, including the ability to stimulate breast cancer invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and evasion from the immune system. This dramatic conversion in TGF-beta function is known as the "TGF-beta paradox" and reflects a variety of dynamic alterations that occur not only within the developing mammary carcinoma, but also within the cellular and structural composition of its accompanying tumor microenvironment. Recent studies have begun to elucidate the critical importance of mammary tumor microenvironments in manifesting the TGF-beta paradox and influencing the response of developing mammary carcinomas to TGF-beta. Here we highlight recent findings demonstrating the essential function of tumor microenvironments in regulating the oncogenic activities of TGF-beta and its stimulation of metastatic progression during mammary tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noncanonical TGF-β signaling during mammary tumorigenesis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011 Jun;16(2):127-46. doi: 10.1007/s10911-011-9207-3. Epub 2011 Mar 31. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 21448580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathophysiology of epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by transforming growth factor-beta in normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010 Jun;15(2):169-90. doi: 10.1007/s10911-010-9181-1. Epub 2010 May 15. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20467795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cain and Abl of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and transforming growth factor-β in mammary epithelial cells.Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;193(1-2):98-113. doi: 10.1159/000320163. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011. PMID: 21051857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta3 integrin and Src facilitate transforming growth factor-beta mediated induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8(4):R42. doi: 10.1186/bcr1524. Breast Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16859511 Free PMC article.
-
Fibulin-5 initiates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and enhances EMT induced by TGF-beta in mammary epithelial cells via a MMP-dependent mechanism.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Dec;29(12):2243-51. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn199. Epub 2008 Aug 19. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18713838 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Contribution of Immune Cells to Glucocorticoid Receptor Expression in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 30;21(13):4635. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134635. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32629782 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora-A kinase oncogenic signaling mediates TGF-β-induced triple-negative breast cancer plasticity and chemoresistance.Oncogene. 2021 Apr;40(14):2509-2523. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01711-x. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33674749 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1 induced deficiency of linc00261 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal-transition and stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma via modulating SMAD3.J Transl Med. 2022 Feb 5;20(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03276-z. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35123494 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal-epithelial crosstalk provides a suitable microenvironment for the progression of ovarian cancer cells in vitro.Cancer Invest. 2013 Nov;31(9):616-24. doi: 10.3109/07357907.2013.849723. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Cancer Invest. 2013. PMID: 24147897 Free PMC article.
-
Native-mimicking in vitro microenvironment: an elusive and seductive future for tumor modeling and tissue engineering.J Biol Eng. 2018 Sep 12;12:20. doi: 10.1186/s13036-018-0114-7. eCollection 2018. J Biol Eng. 2018. PMID: 30220913 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albig A. R.; Schiemann W. P. Fibulin-5 function during tumorigenesis. Future Oncol. 1:23–35; 2005. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni G.; Dejana E. Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions: Molecular organization and role in vascular homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 84:869–901; 2004. - PubMed
-
- Bellone G.; Aste-Amezaga M.; Trinchieri G.; Rodeck U. Regulation of NK cell functions by TGF-β1. J. Immunol. 155:1066–1073; 1995. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
