Neurological complications in HIV
- PMID: 22268312
- PMCID: PMC4952339
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.11-6-571
Neurological complications in HIV
Abstract
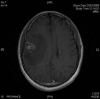
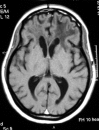
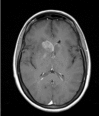
HIV is neuroinvasive with early involvement of the nervous system and has the potential to cause disease at any site of the neuro-axis during the evolution from seroconversion to late stage HIV. Disease may result from direct viral infection, indirect immune-deficiency driven opportunistic infections, AIDS-defining cancers, antiretroviral (ARV) drug therapy, or less well elucidated associations, such as vascular events (Table 1). Recognition of each of these is paramount in the prevention or attenuation of long-term morbidity. Though the epidemiology of neurological disease has altered substantially since the arrival of combination antiretroviral therapy (cART), with reduced incidence and improved survival, the spectrum of central nervous system (CNS) diseases has remained relatively unchanged. Despite available treatment options, mortality remains high and the morbidity significant. CNS diseases can result in long hospital stays, reduced quality of life and marked disability. The majority of disease occurs in the advanced stages of HIV infection where immunosuppression is the predominant influence. Diagnosis can prove challenging as presentation is often atypical and there can be significant neurological involvement with limited evidence of disease. Multiple aetiologies can co-exist and investigations may yield unexpected results, rendering interpretation difficult. Paradoxically, cART may also alter the way CNS disease manifests and unmask opportunistic infections or cause clinical representation of the opportunistic infections, when it represents immune reconstitution syndrome (IRS). Clinical assessment, imaging (typically magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)) and cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) sampling remain the chief diagnostic tools. This conference summary reviews these differing aspects.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical