Beneficial effects of edaravone, a novel antioxidant, in rats with dilated cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 22268705
- PMCID: PMC3822987
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01526.x
Beneficial effects of edaravone, a novel antioxidant, in rats with dilated cardiomyopathy
Abstract
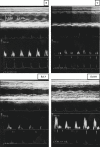
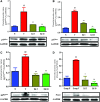
Edaravone, a novel antioxidant, acts by trapping hydroxyl radicals, quenching active oxygen and so on. Its cardioprotective activity against experimental autoimmune myocarditis (EAM) was reported. Nevertheless, it remains to be determined whether edaravone protects against cardiac remodelling in dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). The present study was undertaken to assess whether edaravone attenuates myocardial fibrosis, and examine the effect of edaravone on cardiac function in rats with DCM after EAM. Rat model of EAM was prepared by injection with porcine cardiac myosin 28 days after immunization, we administered edaravone intraperitoneally at 3 and 10 mg/kg/day to rats for 28 days. The results were compared with vehicle-treated rats with DCM. Cardiac function, by haemodynamic and echocardiographic study and histopathology were performed. Left ventricular (LV) expression of NADPH oxidase subunits (p47(phox), p67(phox), gp91(phox) and Nox4), fibrosis markers (TGF-β(1) and OPN), endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress markers (GRP78 and GADD 153) and apoptosis markers (cytochrome C and caspase-3) were measured by Western blotting. Edaravone-treated DCM rats showed better cardiac function compared with those of the vehicle-treated rats. In addition, LV expressions of NADPH oxidase subunits levels were significantly down-regulated in edaravone-treated rats. Furthermore, the number of collagen-III positive cells in the myocardium of edaravone-treated rats was lower compared with those of the vehicle-treated rats. Our results suggest that edaravone ameliorated the progression of DCM by modulating oxidative and ER stress-mediated myocardial apoptosis and fibrosis.
© 2012 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2012 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Kawai C. From myocarditis to cardiomyopathy: mechanisms of inflammation and cell death. Circulation. 2001;34:199–204. - PubMed
-
- Kodama M, Hanawa H, Saeki M, et al. Rat dilated cardiomyopathy after autoimmune giant cell myocarditis. Circ Res. 1994;75:278–84. - PubMed
-
- Okura Y, Yamamoto T, Goto S, et al. Characterization of cytokine and iNOS mRNA expression in situ during the course of experimental autoimmune myocarditis in rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1997;29:491–502. - PubMed
-
- Ishiyama S, Hiroe M, Nishikawa T, et al. The Fas/Fas ligand system is involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune myocarditis in rats. J Immunol. 1998;161:4695–701. - PubMed
-
- Ishiyama S, Hiroe M, Nishikawa T, et al. Nitric oxide contributes the progression of myocardial damage in experimental autoimmune myocarditis in rats. Circulation. 1997;95:489–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

