The transcriptional activator ZNF143 is essential for normal development in zebrafish
- PMID: 22268977
- PMCID: PMC3282657
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-13-3
The transcriptional activator ZNF143 is essential for normal development in zebrafish
Abstract
Background: ZNF143 is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that stimulates transcription of both small RNA genes by RNA polymerase II or III, or protein-coding genes by RNA polymerase II, using separable activating domains. We describe phenotypic effects following knockdown of this protein in developing Danio rerio (zebrafish) embryos by injection of morpholino antisense oligonucleotides that target znf143 mRNA.
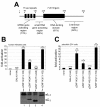
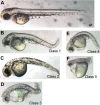
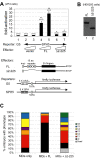
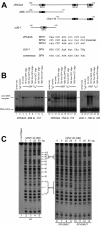
Results: The loss of function phenotype is pleiotropic and includes a broad array of abnormalities including defects in heart, blood, ear and midbrain hindbrain boundary. Defects are rescued by coinjection of synthetic mRNA encoding full-length ZNF143 protein, but not by protein lacking the amino-terminal activation domains. Accordingly, expression of several marker genes is affected following knockdown, including GATA-binding protein 1 (gata1), cardiac myosin light chain 2 (cmlc2) and paired box gene 2a (pax2a). The zebrafish pax2a gene proximal promoter contains two binding sites for ZNF143, and reporter gene transcription driven by this promoter in transfected cells is activated by this protein.
Conclusions: Normal development of zebrafish embryos requires ZNF143. Furthermore, the pax2a gene is probably one example of many protein-coding gene targets of ZNF143 during zebrafish development.
Figures

References
-
- Myslinski E, Krol A, Carbon P. ZNF76 and ZNF143 Are Two Human Homologs of the Transcriptional Activator Staf. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:21998–22006. - PubMed
-
- Myslinski E, Gerard MA, Krol A, Carbon P. A Genome Scale Location Analysis of Human Staf/ZNF143-binding Sites Suggests a Widespread Role for Human Staf/ZNF143 in Mammalian Promoters. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:39953–39962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

