Luteolin decreases IGF-II production and downregulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in HT-29 human colon cancer cells
- PMID: 22269172
- PMCID: PMC3298530
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-9
Luteolin decreases IGF-II production and downregulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in HT-29 human colon cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Luteolin is a 3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone found in various fruits and vegetables. We have shown previously that luteolin reduces HT-29 cell growth by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. The objective of this study was to examine whether luteolin downregulates the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) signaling pathway in HT-29 cells.
Methods: In order to assess the effects of luteolin and/or IGF-I on the IGF-IR signaling pathway, cells were cultured with or without 60 μmol/L luteolin and/or 10 nmol/L IGF-I. Cell proliferation, DNA synthesis, and IGF-IR mRNA levels were evaluated by a cell viability assay, [3H]thymidine incorporation assays, and real-time polymerase chain reaction, respectively. Western blot analyses, immunoprecipitation, and in vitro kinase assays were conducted to evaluate the secretion of IGF-II, the protein expression and activation of IGF-IR, and the association of the p85 subunit of phophatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) with IGF-IR, the phosphorylation of Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2, and cell division cycle 25c (CDC25c), and PI3K activity.
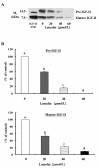
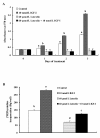
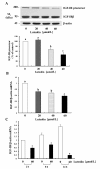
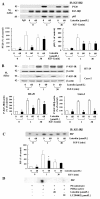
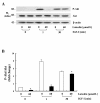
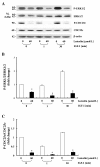
Results: Luteolin (0 - 60 μmol/L) dose-dependently reduced the IGF-II secretion of HT-29 cells. IGF-I stimulated HT-29 cell growth but did not abrogate luteolin-induced growth inhibition. Luteolin reduced the levels of the IGF-IR precursor protein and IGF-IR transcripts. Luteolin reduced the IGF-I-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of IGF-IR and the association of p85 with IGF-IR. Additionally, luteolin inhibited the activity of PI3K activity as well as the phosphorylation of Akt, ERK1/2, and CDC25c in the presence and absence of IGF-I stimulation.
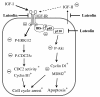
Conclusions: The present results demonstrate that luteolin downregulates the activation of the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways via a reduction in IGF-IR signaling in HT-29 cells; this may be one of the mechanisms responsible for the observed luteolin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conjugated linoleic acid downregulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor levels in HT-29 human colon cancer cells.J Nutr. 2003 Aug;133(8):2675-81. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.8.2675. J Nutr. 2003. PMID: 12888657
-
Fucoidan downregulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor levels in HT-29 human colon cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 Mar;39(3):1516-1522. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6193. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29328495
-
Genistein inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in HT-29 human colon cancer cells: a possible mechanism of the growth inhibitory effect of Genistein.J Med Food. 2005 Winter;8(4):431-8. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2005.8.431. J Med Food. 2005. PMID: 16379552
-
Effects and Mechanisms of Luteolin, a Plant-Based Flavonoid, in the Prevention of Cancers via Modulation of Inflammation and Cell Signaling Molecules.Molecules. 2024 Feb 29;29(5):1093. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051093. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I regulation of immune function: a potential therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases?Pharmacol Rev. 2010 Jun;62(2):199-236. doi: 10.1124/pr.109.002469. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Pharmacol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20392809 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Luteolin attenuates Wnt signaling via upregulation of FZD6 to suppress prostate cancer stemness revealed by comparative proteomics.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 4;8(1):8537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26761-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29867083 Free PMC article.
-
An Association Map on the Effect of Flavonoids on the Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Med Sci. 2016 Apr 29;13(5):374-85. doi: 10.7150/ijms.14485. eCollection 2016. Int J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27226778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Polyphenols for Treatment of Colorectal Cancer.Molecules. 2022 Dec 12;27(24):8810. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248810. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36557939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Insulin-like Growth Factor System and Colorectal Cancer.Life (Basel). 2022 Aug 20;12(8):1274. doi: 10.3390/life12081274. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36013453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular targets of luteolin in cancer.Eur J Cancer Prev. 2016 Jan;25(1):65-76. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0000000000000128. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2016. PMID: 25714651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baserga R, Hongo A, Rubini M, Prisco M, Valentinis B. The IGF-I receptor in cell growth, transformation and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1332(3):F105–126. - PubMed
-
- Dupont J, LeRoith D. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors: similarities and differences in signal transduction. Horm Res. 2001;55(Suppl 2):22–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

