Glutathione transferase pi class 2 (GSTp2) protects against the cardiac deformities caused by exposure to PAHs but not PCB-126 in zebrafish embryos
- PMID: 22269188
- PMCID: PMC3311777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2012.01.007
Glutathione transferase pi class 2 (GSTp2) protects against the cardiac deformities caused by exposure to PAHs but not PCB-126 in zebrafish embryos
Abstract
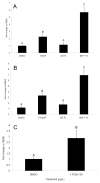
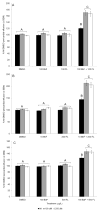
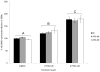
Glutathione transferases (GSTs) are phase II enzymes that detoxify a wide range of toxicants and reactive intermediates. One such class of toxicants is the ubiquitous polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Certain PAHs are known to cause developmental cardiac toxicity in fish. Herein, we explored the role of GST pi class 2 (GSTp2) in PAH- and PCB-induced cardiac toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. We measured expression of GSTp2 in embryos exposed to individual and co-exposures of the PAHs benzo[k]fluoranthene (BkF), benzo[a]pyrene (BaP), and fluoranthene (FL) as well as 3,3',4,4',5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB-126). GSTp2 mRNA expression was induced by exposure to BkF, BaP, PCB-126, and BaP+FL and BkF+FL co-exposure. A splice junction morpholino was then used to knockdown GSTp2 in developing zebrafish. GSTp2 knockdown exacerbated the toxicity caused by co-exposures to BkF+FL and BaP+FL. However, GSTp2 knockdown did not affect PCB-126 toxicity. These results further suggest that pi class GSTs serve a protective function against the synergistic toxicity caused by PAHs in developing zebrafish.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
AHR2 knockdown prevents PAH-mediated cardiac toxicity and XRE- and ARE-associated gene induction in zebrafish (Danio rerio).Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011 Aug 1;254(3):280-7. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2011.05.002. Epub 2011 May 10. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21600235 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of AHR1A but not AHR1B exacerbates PAH and PCB-126 toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos.Aquat Toxicol. 2013 Oct 15;142-143:336-46. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.09.007. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Aquat Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24084256 Free PMC article.
-
AHR2-Mediated transcriptomic responses underlying the synergistic cardiac developmental toxicity of PAHs.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Feb;143(2):469-81. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu245. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25412620 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish cardiotoxicity: the effects of CYP1A inhibition and AHR2 knockdown following exposure to weak aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Jun;22(11):8329-38. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3969-2. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25532870 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CYP1A inhibition in the embryotoxic interactions between hypoxia and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and PAH mixtures in zebrafish (Danio rerio).Ecotoxicology. 2011 Aug;20(6):1300-14. doi: 10.1007/s10646-011-0686-1. Epub 2011 Jun 26. Ecotoxicology. 2011. PMID: 21706407 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effects of CYP1A inhibition on alkyl-phenanthrene metabolism and embryotoxicity in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma).Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Jun;23(11):11289-11297. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6098-2. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26924701
-
Induction and inhibition of human cytochrome P4501 by oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2016 Mar 4;5(3):788-799. doi: 10.1039/c6tx00004e. eCollection 2016 May 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2016. PMID: 30090389 Free PMC article.
-
Teratogenic, bioenergetic, and behavioral effects of exposure to total particulate matter on early development of zebrafish (Danio rerio) are not mimicked by nicotine.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2015 Sep-Oct;51:77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2015. PMID: 26391568 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Functional Roles of the Zebrafish Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptors.Toxicol Sci. 2020 Dec 1;178(2):215-238. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa143. Toxicol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32976604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First application of an Integrated Biological Response index to assess the ecotoxicological status of honeybees from rural and urban areas.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Sep;28(34):47418-47428. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14037-8. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33891238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson T, Pesonen M, Johansson C. Differntial induction of cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase, epoxide hydrolase, glutathione transferease and udp glucuronosyl transferase activities in the liver of rainbow trout by beta-naphthoflavone or Clophen A50. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985;34:3309–3314. - PubMed
-
- Armknecht SL, Kaattari SL, Van Veld PA. An elevated glutathione S-transferase in creosote-resistant mummichog (Fundulus heteroclitus) Aquat Toxicol. 1998;41:1–16.
-
- Bilbao E, Raingeard D, de Cerio OD, Ortiz-Zarragoitia M, Ruiz P, Izagirre U, Orbea A, Marigomez I, Cajaraville MP, Cancio I. Effects of exposure to Prestige-like heavy fuel oil and to perfluorooctane sulfonate on conventional biomarkers and target gene transcription in the thicklip grey mullet Chelon labrosus. Aquat Toxicol. 2010;98:282–296. - PubMed
-
- Billiard SM, Timme-Laragy AR, Wassenberg DM, Cockman C, Di Giulio RT. The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway in mediating synergistic developmental toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to zebrafish. Toxicol Sci. 2006;92:526–536. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn AC, Matthaei KI, Lim C, Taylor MC, Cappello JY, Hayes JD, Anders MW, Board PG. Deficiency of glutathione transferase zeta causes oxidative stress and activation of antioxidant response pathways. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;69:650–657. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

