Heat shock protein 90α (Hsp90α) is phosphorylated in response to DNA damage and accumulates in repair foci
- PMID: 22270370
- PMCID: PMC3308794
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.320887
Heat shock protein 90α (Hsp90α) is phosphorylated in response to DNA damage and accumulates in repair foci
Abstract
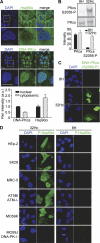
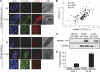
DNA damage triggers a complex signaling cascade involving a multitude of phosphorylation events. We found that the threonine 7 (Thr-7) residue of heat shock protein 90α (Hsp90α) was phosphorylated immediately after DNA damage. The phosphorylated Hsp90α then accumulated at sites of DNA double strand breaks and formed repair foci with slow kinetics, matching the repair kinetics of complex DNA damage. The phosphorylation of Hsp90α was dependent on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-like kinases, including the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) in particular. DNA-PK plays an essential role in the repair of DNA double strand breaks by nonhomologous end-joining and in the signaling of DNA damage. It is also present in the cytoplasm of the cell and has been suggested to play a role in cytoplasmic signaling pathways. Using stabilized double-stranded DNA molecules to activate DNA-PK, we showed that an active DNA-PK complex could be assembled in the cytoplasm, resulting in phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic pool of Hsp90α. In vivo, reverse phase protein array data for tumors revealed that basal levels of Thr-7-phosphorylated Hsp90α were correlated with phosphorylated histone H2AX levels. The Thr-7 phosphorylation of the ubiquitously produced and secreted Hsp90α may therefore serve as a surrogate biomarker of DNA damage. These findings shed light on the interplay between central DNA repair enzymes and an essential molecular chaperone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heat shock protein 90α (HSP90α), a substrate and chaperone of DNA-PK necessary for the apoptotic response.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Aug 7;109(32):12866-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203617109. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22753480 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90α regulates ATM and NBN functions in sensing and repair of DNA double-strand breaks.FEBS J. 2017 Aug;284(15):2378-2395. doi: 10.1111/febs.14145. Epub 2017 Jul 9. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28631426
-
ATM is the primary kinase responsible for phosphorylation of Hsp90α after ionizing radiation.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82450-82457. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12557. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27738310 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90: A New Player in DNA Repair?Biomolecules. 2015 Oct 16;5(4):2589-618. doi: 10.3390/biom5042589. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 26501335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular heat shock protein 90 alpha (eHsp90α)'s role in cancer progression and the development of therapeutic strategies.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Nov 5;277:116736. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116736. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39126794 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hsp70 co-chaperone Ydj1/HDJ2 regulates ribonucleotide reductase activity.PLoS Genet. 2018 Nov 19;14(11):e1007462. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007462. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30452489 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-PK target identification reveals novel links between DNA repair signaling and cytoskeletal regulation.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 25;8(11):e80313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080313. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24282534 Free PMC article.
-
The HSP90 Inhibitor Ganetespib Radiosensitizes Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2015 May 22;7(2):876-907. doi: 10.3390/cancers7020814. Cancers (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26010604 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatase 2A and DNA-dependent protein kinase are involved in mediating rapamycin-induced Akt phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13215-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.463679. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23536185 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic characteristics of resistant tumors to pre-operative ionizing radiation in rectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2014 Jul 15;6(7):194-210. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v6.i7.194. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25024812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wyman C., Kanaar R. (2006) DNA double strand break repair. All's well that ends well. Annu. Rev. Genet. 40, 363–383 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

