Evidence for using bisphosphonate to treat Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
- PMID: 22270467
- PMCID: PMC3830104
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-011-2240-0
Evidence for using bisphosphonate to treat Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
Abstract
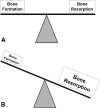
Background: The rationale for using bisphosphonate (BP) therapy for Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (LCPD) is the potential to prevent substantial femoral head deformity during the fragmentation phase by inhibiting osteoclastic bone resorption. However, it is unclear whether BP therapy decreases femoral head deformity.
Questions/purposes: In this systematic review, we answered the following questions: (1) Does bisphosphonate (BP) therapy decrease femoral head deformity and improve pain and function in LCPD or other juvenile osteonecrotic conditions? And (2) does BP therapy decrease femoral head deformity in experimental studies of juvenile femoral head osteonecrosis?
Methods: We searched the literature from 1966 to 2011 for clinical and experimental studies on BP therapy for juvenile femoral head osteonecrosis. Studies specifically addressing clinical and/or radiographic/histologic outcomes pertaining to pain and function and femoral head morphology were analyzed.
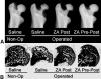
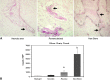
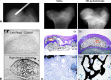
Results: Three Level IV clinical studies met our inclusion criteria. Only one study initiated BP therapy during the precollapsed stage of osteonecrosis and reported prevention of femoral head deformity in nine of 17 patients. All studies noted subjective improvements of pain and gait in patients treated with intravenous BPs. Of the eight experimental studies reviewed, seven reported reduced femoral head deformity and six found better preservation of trabecular framework in animals treated with BPs.
Conclusions: Clinical evidence lacks consistent patient groups and drug protocols to draw definitive conclusions that BP therapy can decrease femoral head deformity in juvenile osteonecrotic conditions. Experimental studies suggest BP therapy protects the infarcted femoral head from deformity, but it lacks bone anabolic effect. Further basic and clinical research are required to determine the potential role of BPs as a medical treatment for LCPD.
Figures


References
-
- Bianchi ML, Cimaz R, Bardare M, Zulian F, Lepore L, Boncompagni A, Galbiati E, Corona F, Luisetto G, Giuntini D, Picco P, Brandi ML, Falcini F. Efficacy and safety of alendronate for the treatment of osteoporosis in diffuse connective tissue diseases in children: a prospective multicenter study. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1960–1966. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9<1960::AID-ANR6>3.0.CO;2-J. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, Cauley JA, Thompson DE, Nevitt MC, Bauer DC, Genant HK, Haskell WL, Marcus R, Ott SM, Torner JC, Quandt SA, Reiss TF, Ensrud KE. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet. 1996;348:1535–1541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

