IRX-2, a novel immunotherapeutic, enhances and protects NK-cell functions in cancer patients
- PMID: 22270713
- PMCID: PMC3721346
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-011-1197-x
IRX-2, a novel immunotherapeutic, enhances and protects NK-cell functions in cancer patients
Abstract
Background: IRX-2 is a primary biologic which has been used for the therapy of head and neck squamous cell cancer (HNSCC) with promising clinical results. Since NK-cell function is compromised in HNSCC patients, we tested the effects of IRX-2 on the restoration of human NK-cell functions in vitro.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were isolated from 23 HNSCC patients and 10 normal controls (NC). The NK-cell phenotype and functions were compared before and after culture ± IRX-2 or ± 50 IU/ml rhIL-2. Flow cytometry was used to study the NK-cell phenotype, cytotoxic activity and cytokine expression.
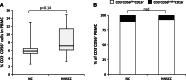
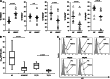
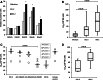
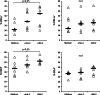
Results: Impaired NK-cell cytotoxicity in HNSCC patients was related to lower expression of NKG2D, NKp30 and NKp46 receptors (P < 0.05) and not to a decreased frequency of NK cells. Incubation of patients' NK cells with IRX-2 up-regulated the percentage of receptor-positive NK cells (P < 0.05). It also up-regulated cytotoxicity of patients' NK cells (P < 0.01) more effectively than rhIL-2 (P < 0.01). IRX-2, but not rhIL-2, protected NK cells from suppression mediated by TGF-β, and it restored (P < 0.05) expression of activating NK-cell receptors and NK-cell cytotoxicity suppressed by TGF-β. Expression of pSMAD was decreased in NK cells treated with IRX-2 but not in those treated with rhIL-2.
Conclusions: IRX-2 was more effective than IL-2 in enhancing NK-cell cytotoxicity and protecting NK-cell function of HNSCC patients in vitro, emphasizing the potential advantage of IRX-2 as a component of future therapies for HNSCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Two of the authors (BS and JEE) received support from IRX Therapeutics Inc. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IRX-2 natural cytokine biologic for immunotherapy in patients with head and neck cancers.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Jun 28;11:3731-3746. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S165411. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29988729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low NKp30, NKp46 and NKG2D expression and reduced cytotoxic activity on NK cells in cervical cancer and precursor lesions.BMC Cancer. 2009 Jun 16;9:186. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-186. BMC Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19531227 Free PMC article.
-
In-vitro IL-2 or IFN-α-induced NKG2D and CD161 NK cell receptor expression indicates novel aspects of NK cell activation in metastatic melanoma patients.Melanoma Res. 2010 Dec;20(6):459-67. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e32833e3286. Melanoma Res. 2010. PMID: 20938360
-
Analysis of the Expression of Surface Receptors on NK Cells and NKG2D on Immunocytes in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Mar 27;19(3):661-665. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.3.661. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 29580037 Free PMC article.
-
The Natural Cytotoxicity Receptors in Health and Disease.Front Immunol. 2019 May 7;10:909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00909. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31134055 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NK cell based immunotherapy against oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 13;15:1440764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1440764. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39192980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impairment of NKG2D-Mediated Tumor Immunity by TGF-β.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 15;10:2689. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02689. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31803194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased immune infiltration and chemokine receptor expression in head and neck epithelial tumors after neoadjuvant immunotherapy with the IRX-2 regimen.Oncoimmunology. 2018 Feb 21;7(5):e1423173. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1423173. eCollection 2018. Oncoimmunology. 2018. PMID: 29721379 Free PMC article.
-
IRX-2 natural cytokine biologic for immunotherapy in patients with head and neck cancers.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Jun 28;11:3731-3746. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S165411. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29988729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Immunotherapeutic Approaches for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2016 Sep 22;8(10):87. doi: 10.3390/cancers8100087. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27669306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wolf GT, Fee WE, Jr, Dolan RW, Moyer JS, Kaplan MJ, Spring PM, Suen J, Kenady DE, Newman JG, Carroll WR, Gillespie MB, Freeman SM, Baltzer L, Kirkley TD, Brandwein HJ, Hadden JW. Novel neoadjuvant immunotherapy regimen safety and survival in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Head Neck. 2011;33:1666–1674. doi: 10.1002/hed.21660. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Freeman SM, Franco JL, Kenady DE, Baltzer L, Roth Z, Brandwein HJ, Hadden JW. A phase 1 safety study of an IRX-2 regimen in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Am J Clin Oncol. 2011;34:173–178. - PubMed
-
- Berinstein NL, Wolf GT, Naylor PH, Baltzer L, Egan JE, Brandwein HJ, Whiteside TL, Goldstein LC, El-Naggar A, Badoual C, Fridman WH, White JM, Hadden JW. Increased lymphocyte infiltration in patients with head and neck cancer treated with the IRX-2 immunotherapy regimen. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

