CXCL12 signaling in the development of the nervous system
- PMID: 22270883
- PMCID: PMC4526243
- DOI: 10.1007/s11481-011-9336-x
CXCL12 signaling in the development of the nervous system
Abstract
Chemokines are small, secreted proteins that have been shown to be important regulators of leukocyte trafficking and inflammation. All the known effects of chemokines are transduced by action at a family of G protein coupled receptors. Two of these receptors, CCR5 and CXCR4, are also known to be the major cellular receptors for HIV-1. Consideration of the evolution of the chemokine family has demonstrated that the chemokine Stromal cell Derived Factor-1 or SDF1 (CXCL12) and its receptor CXCR4 are the most ancient members of the family and existed in animals prior to the development of a sophisticated immune system. Thus, it appears that the original function of chemokine signaling was in the regulation of stem cell trafficking and development. CXCR4 signaling is important in the development of many tissues including the nervous system. Here we discuss the manner in which CXCR4 signaling can regulate the development of different structures in the central and peripheral nervous systems and the different strategies employed to achieve these effects.
Figures

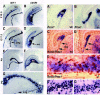
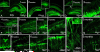
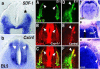
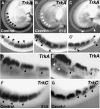
Comment in
-
The molecular basis for neuroimmune receptor signaling.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;7(4):722-4. doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9398-4. Epub 2012 Aug 31. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22935971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso E, Gomez-Santos L, Madrid JF, Saez F. The expression of a novel cxcr4 gene in xenopus embryo. Histol Histopathol. 2009;24:1097–1103. - PubMed
-
- Bagri A, Gurney T, He X, Zou YR, Littman DR, Tessier-Lavigne M, Pleasure SJ. The chemokine SDF regulates migration of dentate granule cells. Development. 2002;129:4249–4260. - PubMed
-
- Bajetto A, Barbero S, Bonavia R, Piccioli P, Pirani P, Florio T, Schettini G. Stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha induces astrocyte proliferation through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 pathway. J Neurochem. 2001a;77:1226–1236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

