Overexpression of a novel cell cycle regulator ecdysoneless in breast cancer: a marker of poor prognosis in HER2/neu-overexpressing breast cancer patients
- PMID: 22270930
- PMCID: PMC3397230
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-011-1946-8
Overexpression of a novel cell cycle regulator ecdysoneless in breast cancer: a marker of poor prognosis in HER2/neu-overexpressing breast cancer patients
Abstract
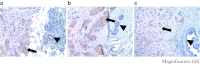
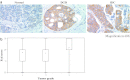
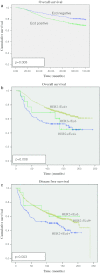
Uncontrolled proliferation is one of the hallmarks of breast cancer. We have previously identified the human Ecd protein (human ortholog of Drosophila Ecdysoneless, hereafter called Ecd) as a novel promoter of mammalian cell cycle progression, a function related to its ability to remove the repressive effects of Rb-family tumor suppressors on E2F transcription factors. Given the frequent dysregulation of cell cycle regulatory components in human cancer, we used immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded tissues to examine Ecd expression in normal breast tissue versus tissues representing increasing breast cancer progression. Initial studies of a smaller cohort without outcomes information showed that Ecd expression was barely detectable in normal breast tissue and in hyperplasia of breast, but high levels of Ecd were detected in benign breast hyperplasia, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDCs) of the breast. In this cohort of 104 IDC patients, Ecd expression levels showed a positive correlation with higher grade (P=0.04). Further analyses of Ecd expression using a larger, independent cohort (954) confirmed these results, with a strong positive correlation of elevated Ecd expression with higher histological grade (P=0.013), mitotic index (P=0.032), and Nottingham Prognostic Index score (P=0.014). Ecd expression was positively associated with HER2/neu (P=0.002) overexpression, a known marker of poor prognosis in breast cancer. Significantly, increased Ecd expression showed a strong positive association with shorter breast cancer specific survival (BCSS) (P=0.008) and disease-free survival (DFS) (P=0.003) in HER2/neu overexpressing patients. Taken together, our results reveal Ecd as a novel marker for breast cancer progression and show that levels of Ecd expression predict poorer survival in Her2/neu overexpressing breast cancer patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Expression of fatty acid synthase and its association with HER2 in invasive ductal carcinoma of breast].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Apr;42(4):257-61. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2013.04.010. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23928534 Chinese.
-
Determination of HER2 phosphorylation at tyrosine 1221/1222 improves prediction of poor survival for breast cancer patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(1):R11. doi: 10.1186/bcr2230. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19239686 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors and c-erbB2 oncogene protein expression in ductal carcinomas of the breast.Cell Biol Int. 2008 Jun;32(6):698-707. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2008.01.007. Epub 2008 Jan 25. Cell Biol Int. 2008. PMID: 18296077
-
HER2 as a prognostic factor in breast cancer.Oncology. 2001;61 Suppl 2:67-72. doi: 10.1159/000055404. Oncology. 2001. PMID: 11694790 Review.
-
In search of triple-negative DCIS: tumor-type dependent model of breast cancer progression from DCIS to the invasive cancer.Tumour Biol. 2013 Feb;34(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0602-1. Epub 2012 Dec 4. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23208673 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Interaction of Ecdysoneless (ECD) Protein with R2TP Complex Component RUVBL1 Is Required for the Functional Role of ECD in Cell Cycle Progression.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Dec 28;36(6):886-99. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00594-15. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26711270 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing for germline mutations in Swedish breast cancer families reveals novel breast cancer risk genes.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 19;11(1):14737. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94316-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34282249 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected role of the steroid-deficiency protein ecdysoneless in pre-mRNA splicing.PLoS Genet. 2014 Apr 10;10(4):e1004287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004287. eCollection 2014 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24722212 Free PMC article.
-
The cell cycle regulator ecdysoneless cooperates with H-Ras to promote oncogenic transformation of human mammary epithelial cells.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(7):990-1000. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1006982. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25616580 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the Nuclear Pool of Ubiquitin Ligase CHIP/STUB1 in Breast Cancer Unleashes the MZF1-Cathepsin Pro-oncogenic Program.Cancer Res. 2018 May 15;78(10):2524-2535. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2140. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29510992 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA087986/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA105489/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA151806/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA116552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA99163/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA099163/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA144027/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01CA151806-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA87986/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA096844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA96844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA144027/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA105489/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

