PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in patients with breast and gynecologic malignancies harboring PIK3CA mutations
- PMID: 22271473
- PMCID: PMC3295566
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.1196
PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in patients with breast and gynecologic malignancies harboring PIK3CA mutations
Abstract
Purpose: Mutations of the PIK3CA gene may predict response to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors. Concomitant mutations in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway may mediate resistance.
Patients and methods: Tumors from patients with breast, cervical, endometrial, and ovarian cancer referred to the Clinical Center for Targeted Therapy (Phase I Program) were analyzed for PIK3CA, KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF mutations. Patients with PIK3CA mutations were treated, whenever feasible, with agents targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
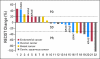
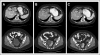
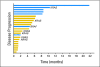
Results: Of 140 patients analyzed, 25 (18%) had PIK3CA mutations, including five of 14 patients with squamous cell cervical, seven of 29 patients with endometrial, six of 29 patients with breast, and seven of 60 patients with ovarian cancers. Of the 25 patients with PIK3CA mutations, 23 (median of two prior therapies) were treated on a protocol that included a PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitor. Two (9%) of 23 patients had stable disease for more than 6 months, and seven patients (30%) had a partial response. In comparison, only seven (10%) of 70 patients with the same disease types but with wild-type PIK3CA treated on the same protocols responded (P = .04). Seven patients (30%) with PIK3CA mutations had coexisting MAPK pathway (KRAS, NRAS, BRAF) mutations (ovarian cancer, n = 5; endometrial cancer, n = 2), and two of these patients (ovarian cancer) achieved a response.
Conclusion: PIK3CA mutations were detected in 18% of tested patients. Patients with PIK3CA mutations treated with PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors demonstrated a higher response rate than patients without mutations. A subset of patients with ovarian cancer with simultaneous PIK3CA and MAPK mutations responded to PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors, suggesting that not all patients demonstrate resistance when the MAPK pathway is concomitantly activated.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Tumor genetic testing for patient selection in phase I clinical trials: the case of PI3K inhibitors.J Clin Oncol. 2012 Mar 10;30(8):765-6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.39.6390. Epub 2012 Jan 23. J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22271482 No abstract available.
References
-
- Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1031–1037. - PubMed
-
- Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Blanke CD, et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:472–480. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

