Gradual increase of miR156 regulates temporal expression changes of numerous genes during leaf development in rice
- PMID: 22271747
- PMCID: PMC3291253
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.190488
Gradual increase of miR156 regulates temporal expression changes of numerous genes during leaf development in rice
Abstract
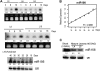
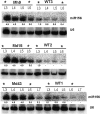
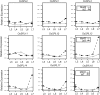
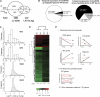
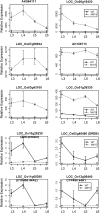
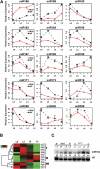
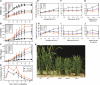
The highly conserved plant microRNA, miR156, is an essential regulator for plant development. In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), miR156 modulates phase changing through its temporal expression in the shoot. In contrast to the gradual decrease over time in the shoot (or whole plant), we found that the miR156 level in rice (Oryza sativa) gradually increased from young leaf to old leaf after the juvenile stage. However, the miR156-targeted rice SQUAMOSA-promoter binding-like (SPL) transcription factors were either dominantly expressed in young leaves or not changed over the time of leaf growth. A comparison of the transcriptomes of early-emerged old leaves and later-emerged young leaves from wild-type and miR156 overexpression (miR156-OE) rice lines found that expression levels of 3,008 genes were affected in miR156-OE leaves. Analysis of temporal expression changes of these genes suggested that miR156 regulates gene expression in a leaf age-dependent manner, and miR156-OE attenuated the temporal changes of 2,660 genes. Interestingly, seven conserved plant microRNAs also showed temporal changes from young to old leaves, and miR156-OE also attenuated the temporal changes of six microRNAs. Consistent with global gene expression changes, miR156-OE plants resulted in dramatic changes including precocious leaf maturation and rapid leaf/tiller initiation. Our results indicate that another gradient of miR156 is present over time, a gradual increase during leaf growth, in addition to the gradual decrease during shoot growth. Gradually increased miR156 expression in the leaf might be essential for regulating the temporal expression of genes involved in leaf development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The heterochronic gene Oryza sativa LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN 1 modulates miR156b/c/i/e levels.J Integr Plant Biol. 2020 Dec;62(12):1839-1852. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12991. Epub 2020 Aug 12. J Integr Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32644250
-
Loose Plant Architecture1, an INDETERMINATE DOMAIN protein involved in shoot gravitropism, regulates plant architecture in rice.Plant Physiol. 2013 Jan;161(1):317-29. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208496. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23124325 Free PMC article.
-
Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell. 2008 May;20(5):1231-43. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.058180. Epub 2008 May 20. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18492871 Free PMC article.
-
Juvenile Leaves or Adult Leaves: Determinants for Vegetative Phase Change in Flowering Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 21;21(24):9753. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249753. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33371265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The integration of leaf-derived signals sets the timing of vegetative phase change in maize, a process coordinated by epigenetic remodeling.Plant Sci. 2021 Nov;312:111035. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.111035. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34620439 Review.
Cited by
-
The hot pepper (Capsicum annuum) microRNA transcriptome reveals novel and conserved targets: a foundation for understanding MicroRNA functional roles in hot pepper.PLoS One. 2013 May 30;8(5):e64238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064238. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23737975 Free PMC article.
-
smartPARE: An R Package for Efficient Identification of True mRNA Cleavage Sites.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 20;22(8):4267. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084267. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33924042 Free PMC article.
-
Switchgrass SBP-box transcription factors PvSPL1 and 2 function redundantly to initiate side tillers and affect biomass yield of energy crop.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016 May 5;9:101. doi: 10.1186/s13068-016-0516-z. eCollection 2016. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016. PMID: 27158262 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic improvement of the shoot architecture and yield in soya bean plants via the manipulation of GmmiR156b.Plant Biotechnol J. 2019 Jan;17(1):50-62. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12946. Epub 2018 May 23. Plant Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 29729214 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of microRNAs and Target Genes in Musa acuminata subsp. burmannicoides, var. Calcutta 4 during Interaction with Pseudocercospora musae.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;12(7):1473. doi: 10.3390/plants12071473. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asai K, Satoh N, Sasaki H, Satoh H, Nagato Y. (2002) A rice heterochronic mutant, mori1, is defective in the juvenile-adult phase change. Development 129: 265–273 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

