Overexpression of FoxM1 offers a promising therapeutic target in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 22271891
- PMCID: PMC3396683
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2011.053421
Overexpression of FoxM1 offers a promising therapeutic target in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: FoxM1 has been shown to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of various epithelial malignancies. However, its role in lymphoid malignancies has not been fully clarified. We, therefore, investigated the role of FoxM1 expression in a large cohort of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma samples and panel of cell lines.
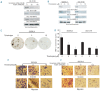
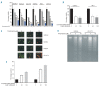
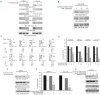
Design and methods: FoxM1 expression was investigated in a large series of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma tissues in a tissue microarray format by immunohistochemistry. Apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry and protein expression was detected by immunoblotting using diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell lines following treatment with either pharmacological inhibitor of FoxM1 or small interference RNA knockdown strategy. Invasion/migration and soft agar colony assays were also performed following treatment with FoxM1 inhibitor.
Results: FoxM1 expression was detected in 84.6% of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma tumors and found to be significantly associated with proliferative tumor marker Ki67 (P<0.0001), matrix metalloproteinases-2 (P=0.0008), matrix metalloproteinases-9 (P=0.0002), S-phase kinase associated protein-2 (P<0.0001) and inversely associated with p27 expression (P=0.0215). Expression of small interference RNA targeted against FoxM1 or treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells with thiostrepton caused its downregulation accompanied by decreased expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and matrix metalloproteinases-9. Inhibition of FoxM1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells also decreased invasive and migratory capability, and induced caspase dependent apoptosis via activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Finally, combined thiostrepton and bortezomib at sub-toxic doses led to efficient apoptosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells.
Conclusions: Altogether, these results suggest that FoxM1 is over-expressed in the majority of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma samples. These data also indicate that targeting FoxM1 signaling can serve as a potential therapeutic modality in the management of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Figures

References
-
- Escalon MP, Lossos IS. Pharmacotherapy of large B-cell lymphoma. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9(13):2247–58. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RI. Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone versus intensive chemotherapy in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997;40(Suppl):S42–6. - PubMed
-
- Markovic O, Marisavljevic D, Cemerikic V, Perunicic M, Savic S, Filipovic B, et al. Clinical and prognostic significance of apoptotic profile in patients with newly diagnosed nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) Eur J Haematol. 2011;86(3):246–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

