Defective erythroid maturation in gelsolin mutant mice
- PMID: 22271892
- PMCID: PMC3396666
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2011.052522
Defective erythroid maturation in gelsolin mutant mice
Abstract
Background: During late differentiation, erythroid cells undergo profound changes involving actin filament remodeling. One of the proteins controlling actin dynamics is gelsolin, a calcium-activated actin filament severing and capping protein. Gelsolin-null (Gsn(-/-)) mice generated in a C57BL/6 background are viable and fertile.1
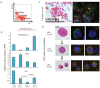
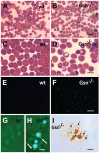
Design and methods: We analyzed the functional roles of gelsolin in erythropoiesis by: (i) evaluating gelsolin expression in murine fetal liver cells at different stages of erythroid differentiation (using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis and immunohistochemistry), and (ii) characterizing embryonic and adult erythropoiesis in Gsn(-/-) BALB/c mice (morphology and erythroid cultures).
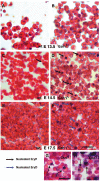
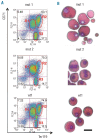
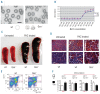
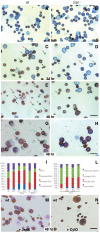
Results: In the context of a BALB/c background, the Gsn(-/-) mutation causes embryonic death. Gsn(-/-) embryos show defective erythroid maturation with persistence of circulating nucleated cells. The few Gsn(-/-) mice reaching adulthood fail to recover from phenylhydrazine-induced acute anemia, revealing an impaired response to stress erythropoiesis. In in vitro differentiation assays, E13.5 fetal liver Gsn(-/-) cells failed to undergo terminal maturation, a defect partially rescued by Cytochalasin D, and mimicked by administration of Jasplakinolide to the wild-type control samples.
Conclusions: In BALB/c mice, gelsolin deficiency alters the equilibrium between erythrocyte actin polymerization and depolymerization, causing impaired terminal maturation. We suggest a non-redundant role for gelsolin in terminal erythroid differentiation, possibly contributing to the Gsn(-/-) mice lethality observed in mid-gestation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of actin filament stabilization on adult hippocampal and olfactory bulb neurogenesis.J Neurosci. 2010 Mar 3;30(9):3419-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4231-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20203201 Free PMC article.
-
Role of gelsolin in the actin filament regulation of cardiac L-type calcium channels.Am J Physiol. 1999 Dec;277(6):C1277-83. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1999.277.6.C1277. Am J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10600780
-
Gelsolin is expressed in early erythroid progenitor cells and negatively regulated during erythropoiesis.J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1425-33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1425. J Cell Biol. 1987. PMID: 2821013 Free PMC article.
-
Primitive erythropoiesis in the mammalian embryo.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(6-7):1011-8. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.093056jp. Int J Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20711979 Review.
-
Structure, regulation and related diseases of the actin-binding protein gelsolin.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2019 Jan 30;20:e7. doi: 10.1017/erm.2018.7. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30698126 Review.
Cited by
-
Cdk6 contributes to cytoskeletal stability in erythroid cells.Haematologica. 2017 Jun;102(6):995-1005. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.159947. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 28255017 Free PMC article.
-
Erythroid enucleation: a gateway into a "bloody" world.Exp Hematol. 2021 Mar;95:13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2021.01.001. Epub 2021 Jan 10. Exp Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33440185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium Signaling Is Required for Erythroid Enucleation.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 5;11(1):e0146201. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146201. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26731108 Free PMC article.
-
The modern primitives: applying new technological approaches to explore the biology of the earliest red blood cells.ISRN Hematol. 2013 Oct 3;2013:568928. doi: 10.1155/2013/568928. ISRN Hematol. 2013. PMID: 24222861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secreted gelsolin inhibits DNGR-1-dependent cross-presentation and cancer immunity.Cell. 2021 Jul 22;184(15):4016-4031.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.021. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34081922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Witke W, Sharpe AH, Hartwig JH, Azuma T, Stossel TP, Kwiatkowski DJ. Hemostatic, inflammatory, and fibroblast responses are blunted in mice lacking gelsolin. Cell. 1995;81(1):41–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

